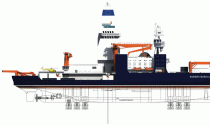
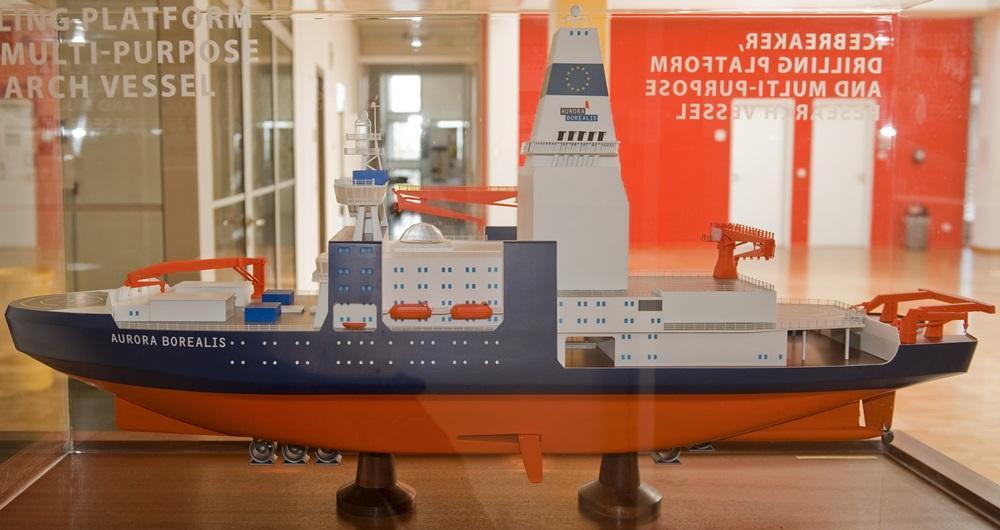
Aurora Borealis icebreaker
Cruise line
Icebreakers
Specifications of Aurora Borealis icebreaker
| Year of build | 2025 new ship |
| Class | diesel icebreaker (Ice class PC1) |
| Building cost | EUR 500 million (USD 670 million) |
| Propulsion power | 27 MW / 36208 hp |
| Speed | 15 kn / 28 km/h / 17 mph |
| Length (LOA) | 200 m / 656 ft |
| Beam (width) | 49 m / 161 ft |
| Crew | 120 |
Aurora Borealis icebreaker Review
Review of Aurora Borealis icebreaker
Aurora Borealis icebreaker is a European project for building the world's largest icebreaking vessel. The project is a joint venture of a total of 15 participating EU (European Union) companies and organizations from all 10 EU nations. When built, the ship will be not only the world's largest icebreaker but also the world's first ever vessel that combines as functions Icebreaker (of the highest ice class PC1), seabed drilling platform and multi-purpose polar research Vessel.
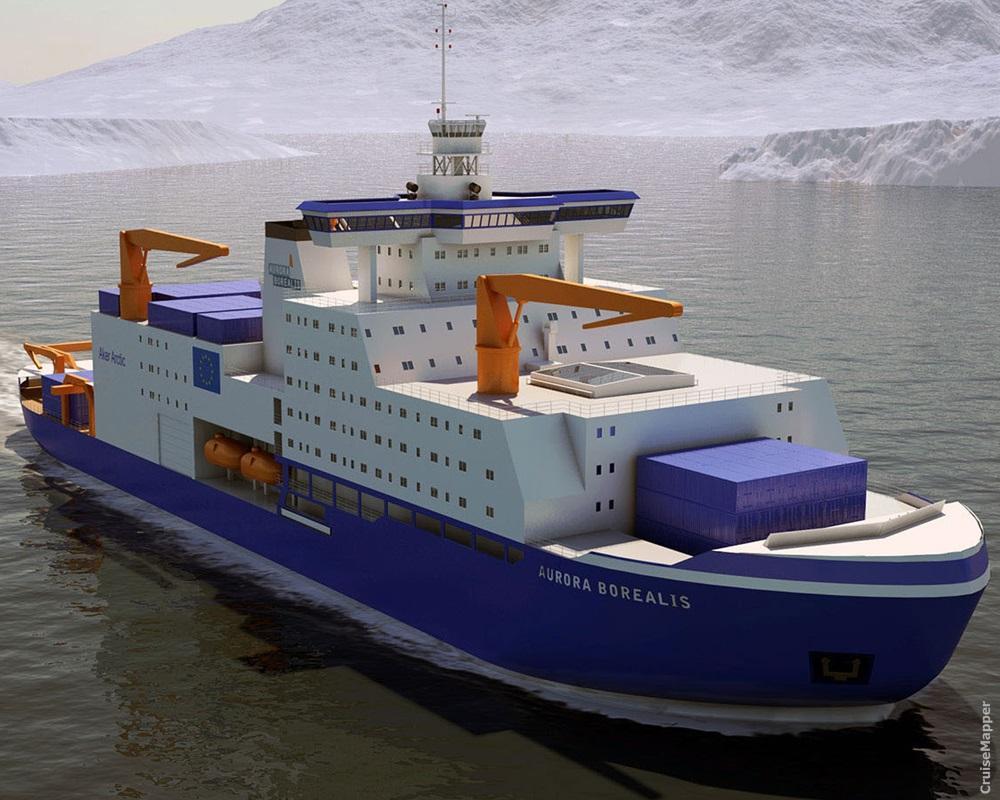

A unique feature of the icebreaker is its ability for scientific deep sea seabed drilling in ice-covered ocean waters. The ship has 35-40 years operational lifetime and will operate on year-round scientific cruises with itineraries in the Arctic Ocean and along Antarctica's continental shelf. The vessel will be operated routinely and without the need for additional icebreaking support. The list of scientific disciplines that will be served by the icebreaker includes Biology, Glaciology (ice/glaciers studies), Geology, Geophysics, Oceanography, Bathymetry (underwater depth studies), Meteorology (climate and environmental research), Atmospheric Physics and Chemistry.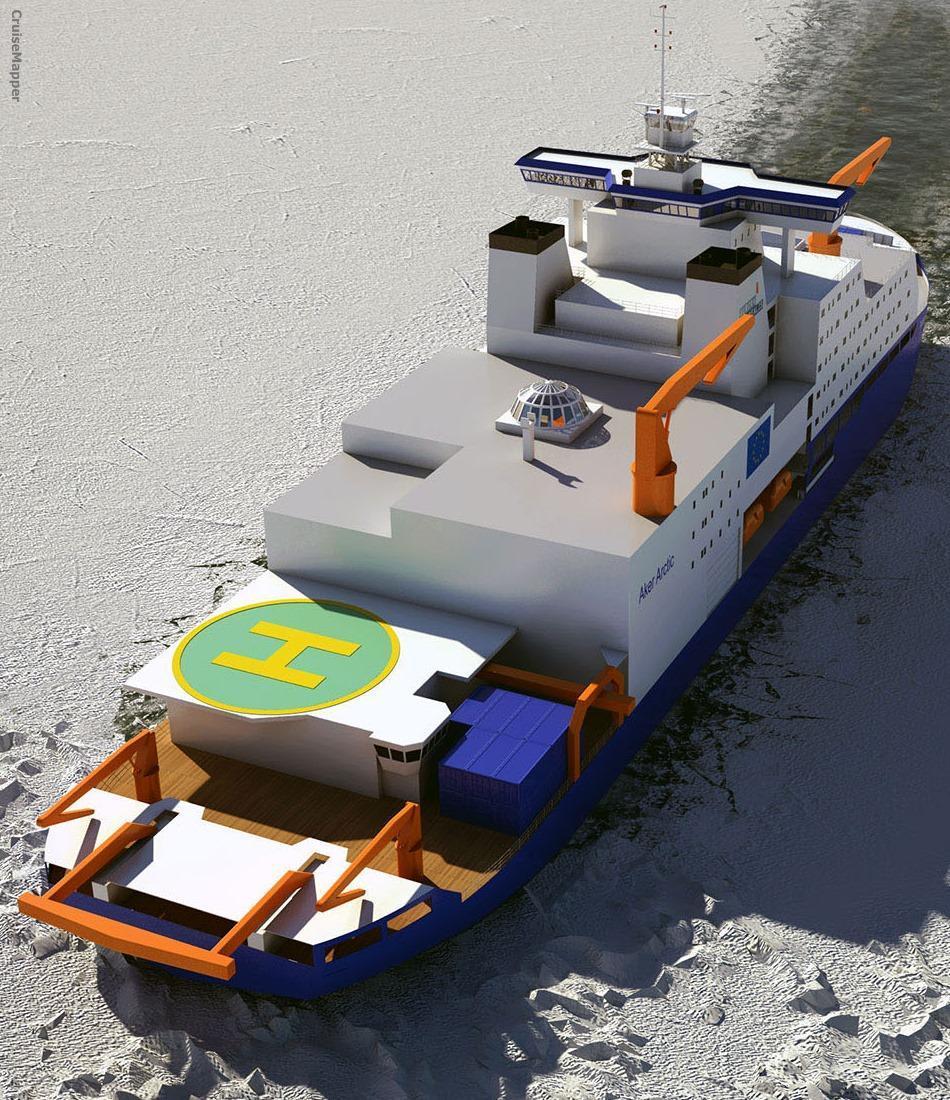
The project impacts two differently specialized scientific communities - the polar science community (to conduct year-round land and marine works) and the deep-sea drilling industry (chartering the vessel mainly during summer to study the Arctic Ocean's seabed structure and properties). The icebreaker Aurora Borealis will be operated by Consortium Partners and chartered to various EU countries and also to other partner nations.
- The ship's planning was started in 2002. The project is under the European Science Foundation's umbrella and coordinated by the European Polar Board (independent EU organization).
- The Aurora Borealis project's preparations in the period March 2007 through -January 2009 were funded (EUR 5,2 million / USD 6,9 million) by Germany's "Ministry for Science and Education". The project's final engineering works were carried out under the coordination of Alfred Wegener Institute (Polar and Marine Research)) in Bremerhaven Germany.
- The development project's duration was set for the period 2008 (March 1) through 2012 (February 28).
- The ship's design was developed by Schiffko - Wartsila Corporation's marine design division (based in Hamburg Germany). In December 2008, the icebreaker's technical design was presented in Berlin Germany by Schiffko and the Alfred Wegener Institute.
The project's planned realization was construction works to start in 2012 and the vessel to be launched (commissioned) in 2014. However, Germany's support for the EUR 800 million (USD 1,07 billion) icebreaker project was stopped in January 2009, when the project has been delayed and its future remains uncertain.
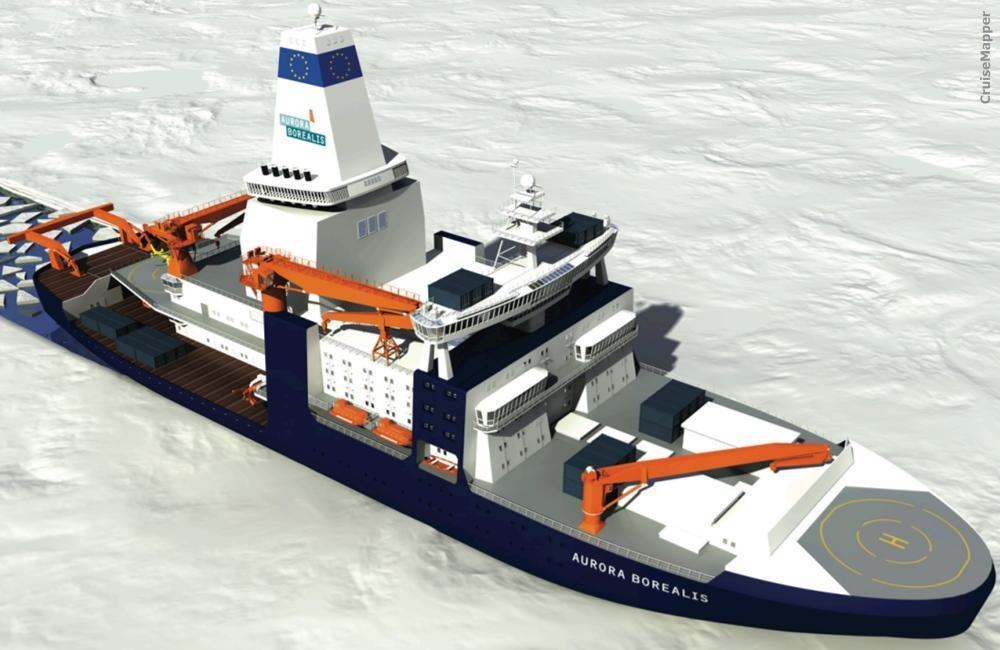

In March 2012, the icebreaker's revised (more cost-effective) version "Aurora Slim" was developed and presented by Aker Arctic Technology Inc - marine engineering company founded in 2004 and headquartered in Helsinki Finland.
- The estimated budget for the new icebreaker ("Aurora Slim" version) was around EUR 500 million (USD 670 million / construction costs) plus EUR 36 million (USD 48 million / operational costs).
- Unlike the original Aurora Borealis, the Aurora Slim design has no onboard installed drilling rig. Instead, for seabed drilling is used a mobile drilling platform allowing operations in shallower waters (up to 1 km / 3300 ft) under polar conditions. The water depth for the original icebreaker design was over 5 km (16400 ft) deep-sea drilling under polar conditions.
- Also unlike the bigger version, instead 2 moon pools Aurora Slim has only one. The ship's dynamical positioning (propulsion) system consists of three Azimuth thrusters (power output 15 MW each) and two bow thrusters (power output 3,5 MW each). The original propulsion design was with three propeller shafts (AC propulsion motors with combined power output 81 MW) plus six Wartsila Transverse Thrusters (retractable, 2 x 3 units / forward and aft set, combined power output 13,5 MW).
- The original icebreaker's drilling rig had a length of 85 m (279 ft / above keel) and loading capacity of 680 tons.

The list of EU countries (participants/organizations) involved in this project includes:
- France (European Science Foundation, and the National Centre for Scientific Research)
- Germany (Alfred Wegener Institute for Polar and Marine Research, and Federal Ministry of Education and Research)
- Italy (National Research Council, and National Antarctic Research Program)
- Russia (Arctic and Antarctic Research Institute)
- Finland (Finnish Institute of Marine Research, and Aker Arctic)
- Holland (Netherlands Organisation for Scientific Research)
- Norway (Bergen University)
- Belgium (National Fund for Scientific Research)
- Bulgaria (Bulgarian Antarctic Institute)
- Romania (Antarctica Romana Foundation)
Aurora Borealis icebreaker vessel details
The icebreaker is powered by 8 main marine diesel engines (generator sets) with combined max power output 94 MW / electric). Additional are emergency generators, waste heat recovery system, exhaust gas cleaning system.
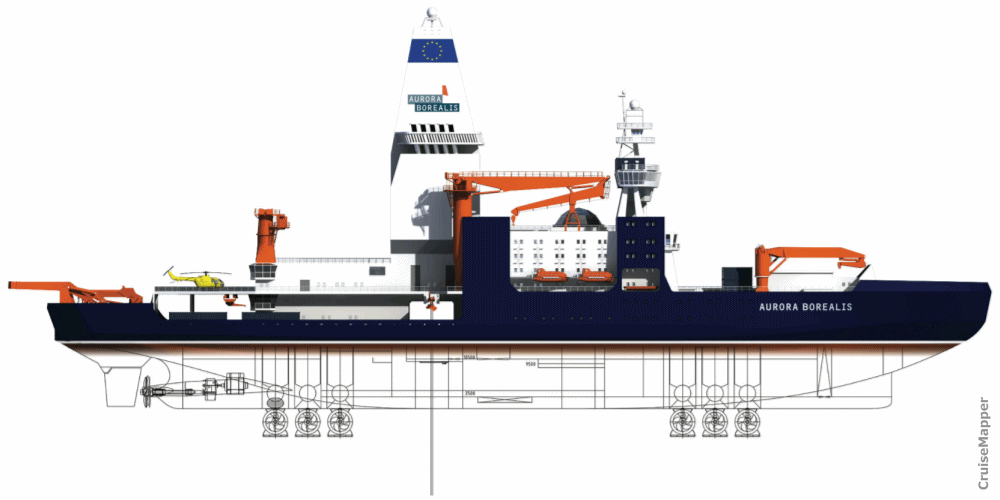
The ship's diesel-electric propulsion (Aurora Slim version) consists of 3x Azimuth thrusters (combined power output 45 MW) plus 2x bow thrusters (combined power output 7 MW).
- Hull design: twin hull, with sloped sidewalls (enabling it to break the ice during dynamic positioning
- Anti-Heeling System - when tilts sideways (portside or starboard) the ship doesn't return back to its upright position. The ice-strengthened propellers are protected from the ice going beneath the hull during icebreaking. The swath bathymetry (underwater sounding equipment) and the sediment echo-sounders are positioned in the ice keel (before the bow thrusters).
- DWT Deadweight tonnage: TBA tons
- Displacement tonnage: 65000 tons
- Max Draught: 13 m (43 ft)
- Icebreaking capacity: 2,5 m (8,2 ft) in both directions (forward and backward) and in drifting ice at speed 2-3 Kn (3,7-5,5 kph / 2,3-3,5 mph)
- Ice-class: PC1 ("Polar Class 1") world's highest
- Endurance: 90 days
- Max speed: 15,5 Kn (28,7 kph / 17,8 mph) in open water
- Cruising speed: 12 kN (22 kph / 14 mph) in open water
- Operational temperature range: 30 C, to +45 C
- Capacity: 120 (crew and passengers)
- Staterooms: 100 (of which 80 single-bed and 20 double-bed cabins)
- Helipads: 2 (helicopter landing decks) plus 1 hangar (capacity 3 helicopters). The hangar can also be used as a cargo storage facility for various equipment and also for containerized (mobile) labs.
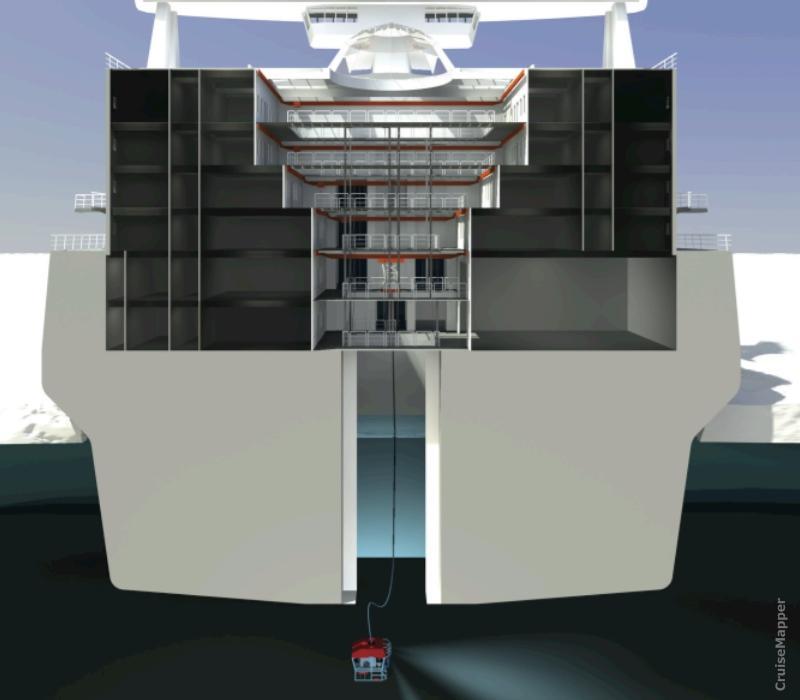
- Moonpools on the original Aurora Borealis vessel were two - one used for scientific drilling, and one used for deployment of other submersible equipment. Each moon pool is sized 7x7 m (23x23 ft).
- The "moon pool" is a unique design feature of marine drilling vessels/platforms and also of diving support- and some underwater research vessels. It allows deployment of submersible machinery, which on the Aurora Borealis icebreaker includes ROVs ("Remotely Operated Vehicle") and AUVs ("Autonomous Underwater Vehicle") that can be deployed in ice conditions. Next image shows the ship's moonpool and an ROV deployment.

Note: In the case of poor AIS coverage, tracking the vessel's current location will be impossible. You can see the CruiseMapper's list of all icebreakers and ice-breaking research ships in the "itinerary" section of our Icebreakers hub. All states and their fleets are listed there.