NS Rossiya icebreaker
Cruise line
Rosatom-Rosmorport Russia (Icebreakers)
Specifications of NS Rossiya icebreaker
| Year of build | 2027 new ship |
| Builder | SKK Zvezda Shipbuilding Complex (Bolshoy Kamen, Russia). |
| Class | Russian nuclear icebreaker (Leader-class, Project 10510) |
| Building cost | RUB 127,5 billion (USD 1,99B / EUR 1,56B) |
| Speed | 23 kn / 43 km/h / 26 mph |
| Length (LOA) | 209 m / 686 ft |
| Beam (width) | 48 m / 157 ft |
| Passengers | 12 |
| Crew | 127 |
| Decks | 7 |
| Decks with cabins | 3 |
| Christened by | tba |
| Owner | Russian Federation (via FSUE Atomflot) |
| Operator | Atomflot (Rosmorport) |
NS Rossiya icebreaker Review
Review of NS Rossiya icebreaker
NS Rossiya ("атомный ледокол Россия") is the first in a 3-unit series of "Project 10510" (aka Project Lider/Leader, aka LK-120Ya) Russian nuclear icebreakers. "NS" stands for "nuclear ship". The vessel is state-owned (by the Russian Federation via FSUE Atomflot) and operated by Rosatom. The Atomflot company provides all Russian nuclear icebreakers with maintenance and technological services. The company also serves the country's special vessel fleet.
The vessel (IMO number 9911238) is Russia-flagged (MMSI tba) and registered in Murmansk.
NS Rossiya is currently scheduled for completion and commissioning in 2027 December. Construction works on the other two Project 10510 sisterships are currently planned to start in 2023 (tbn2/2030-completed/IMO 9945930) and 2025 (tbn3/2032-completed/IMO 9945942).
Besides NS Sibir, the list of Russian nuclear icebreaker ships includes Taymyr (1989), Vaygach (1990), Yamal (1992), 50 Let Pobedy (2007), Arktika (2020), Sibir (2021), Ural (2022), Yakutia (2024), Chukotka (2026), Leningrad (2028), Stalingrad (2030), Sevmorput (1988/cargo ship).
Project 10510 icebreakers - history and construction
Plans for the design and construction of a new class of 110-MW nuclear icebreakers were first announced in September 2011. The project was initiated shortly afterward, with the state-owned Krylov State Research Center (Крыловский государственный научный центр/shipbuilding research and development institute) starting to develop the design in co-operation with "CDB-Iceberg" (ЦКБ Айсберг/Central Design Bureau Iceberg), which is a subsidiary of USC-United Shipbuilding Corporation (also the owner of Arctech Helsinki Shipyard).
Project 10510 nuclear icebreakers are intended for escort services along the Northern Sea Route (Се́верный морско́й путь). The shipping route runs along Russia's Arctic coast/Siberia -from Kara Sea to the Bering Strait. The new icebreakers can escort and assist cargo ships, LNG carriers and oil tankers with max width 50 m (160 ft) and max DWT-Deadweight 100,000 tonnes.
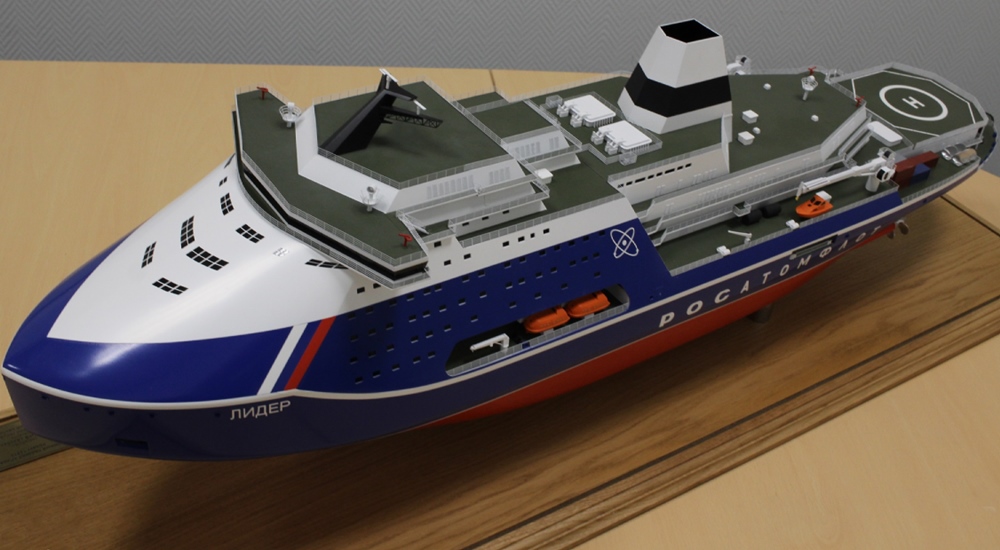

In February 2019 was officially confirmed that the shipbuilder of all the three Project 10510 icebreakers is Zvezda Shipbuilding Complex (Судостроительный комплекс Звезда/2015-founded) that operates Russia's country's largest shipyard Zvezda (located in Bolshoy Kamen, Primorsky Krai).
On January 15, 2020, Russia's Prime Minister signed an order for allocation of RUB 125,57 billion (USD 1,959B / EUR 1,77B) from the federal budget for the construction of the first unit. On April 23, 2020, Atomflot signed with SKK-Zvezda the contract for the construction of NS Rossiya (the first Project 10510 ship).
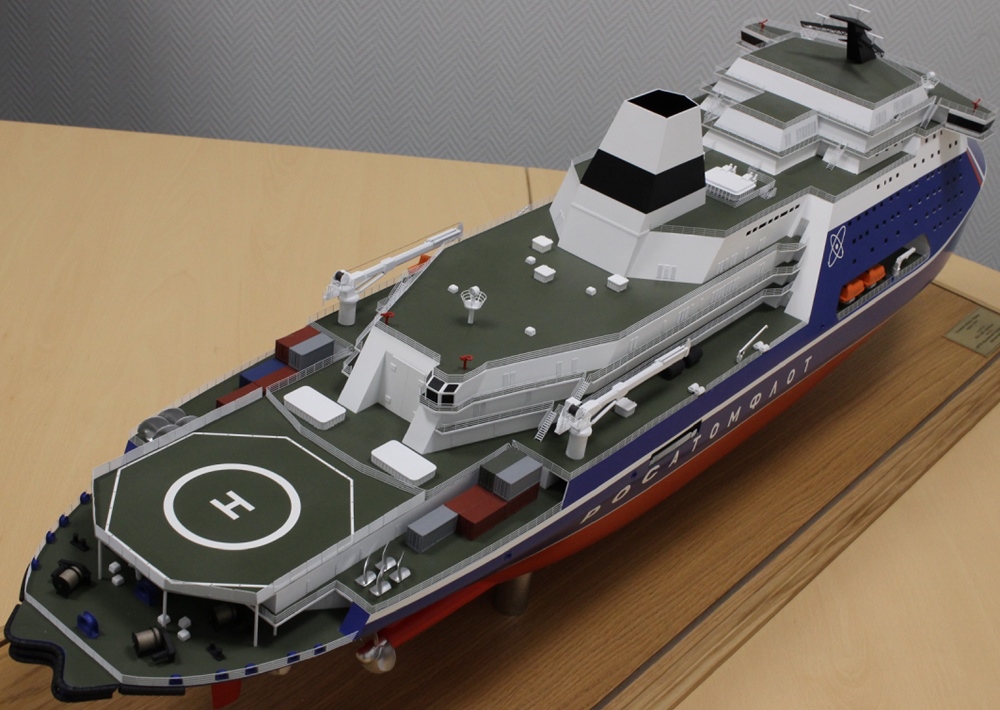

NS Rossiya's construction officially started on July 6, 2020 (steel-cutting ceremony, hull/yard number 056). The keel-laying ceremony was held on July 5, 2021. The vessel's launch/float out from drydock is currently planned for 2025.
NS Rossiya vessel details
Project Leader icebreakers are designed with intended lifespan/service life of 40 years.
- Min Draft: 11,5 m (38 ft)
- Max Draft: 13 m (43 ft)
- DWT-Deadweight tonnage: 100,000 tonnes
- Displacement tonnage: 50,398 tonnes (standard), 70,674 tonnes (full-load)
- Icebreaking capacity: 4,3 m (14 ft) at speed 2 kn / 3,7 kph / 2,3 mph
- Max icebreaking capacity: 5 m (16 ft)
- Range: unlimited (8 months endurance without bunkering/refueling)
- Powerplant: two RITM-400 nuclear reactors (each 315 MW, or 630 MW combined power output)
- Propulsion: turbo-electric, 4 shafts, 4 electric motors (30 MW output each, or 120 MW combined power output), 4x FPPs/fixed pitch propellers (each with 4x removable blades)
- Aft Helideck
The RITM-400 is a larger version of the RITM-200 nuclear reactor developed by Rosatom's subsidiary company OKBM Afrikantov (nuclear engineering company in Nizhny Novgorod). RITM-200 itself is an improvement of the KLT-40 nuclear fission reactors, preceded by the ship reactors OK-150 and OK-900. All these floating powerplants are with lifespan 60 years, fuel cycle 6 years (require refueling every 10 years) and use up to 20% enriched Uranium-235.
The vessel's speed is depending on ice conditions/thickness: 23 knots (in clean water), 15 knots (2-m / 7-ft ice), 2 knots (4,3-m / 14-ft ice).
For information regarding the old Rossiya icebreaker (1985-built/2013-decommissioned) see the ship's Wiki page.
Note: In the case of poor AIS coverage, tracking the vessel's current location will be impossible.
You can see CruiseMapper's list of all icebreakers and ice-breaking research ships in the "itinerary" section of our Icebreakers hub. All states and their fleets are listed there.
NS Rossiya icebreaker - user reviews and comments
Other Rosatom-Rosmorport Russia cruise ships
NS Rossiya icebreaker Wiki
ROSATOM (2007-founded) is a state-owned nuclear energy corporation headquartered in Moscow. It comprises over 360 companies and organizations, specializing in scientific research and nuclear weapons, as well as the world's only fleet of nuclear icebreakers. In 2017, ROSATOM produced 202,868 billion kWh of electricity annually or 18,9% of Russia's total electricity. Corporation's construction projects include 33 nuclear powerplant units installed and maintained in 12 countries. It also manufactures related equipment, produces isotopes for nuclear medicine, conducts research and studies, produces supercomputers and software, develops renewable energy technologies (including wind turbines). ROSATOM covers 17,7% of the world's nuclear fuel market and ~35% market share of the global Uranium enrichment services.
The old Rossiya icebreaker
The old vessel (IMO number 8424240) was Russia-flagged (MMSI 273133400) and registered in Murmansk. It was officially decommissioned in 2013 (following the winter 2012-13 deployment in the Gulf of Finland) and is currently laid up (still not scrapped).
One of the largest Russian icebreaker ships, Rossiya is a nuclear-powered icebreaking vessel of the Arktika-class. Its construction (hull/yard number 702) started on February 20, 1981, with the keel-layin), the launch/float out from drydock was on November 2, 1983, and was delivered/commissioned on December 20, 1985.
Besides NS Rossiya, the list of other Russian nuclear icebreaker ships includes Arktika (2017), Sibir (2021), Taymyr (1989), Ural (2022), Vaygach (1990), Sevmorput (1988, cargo ship).
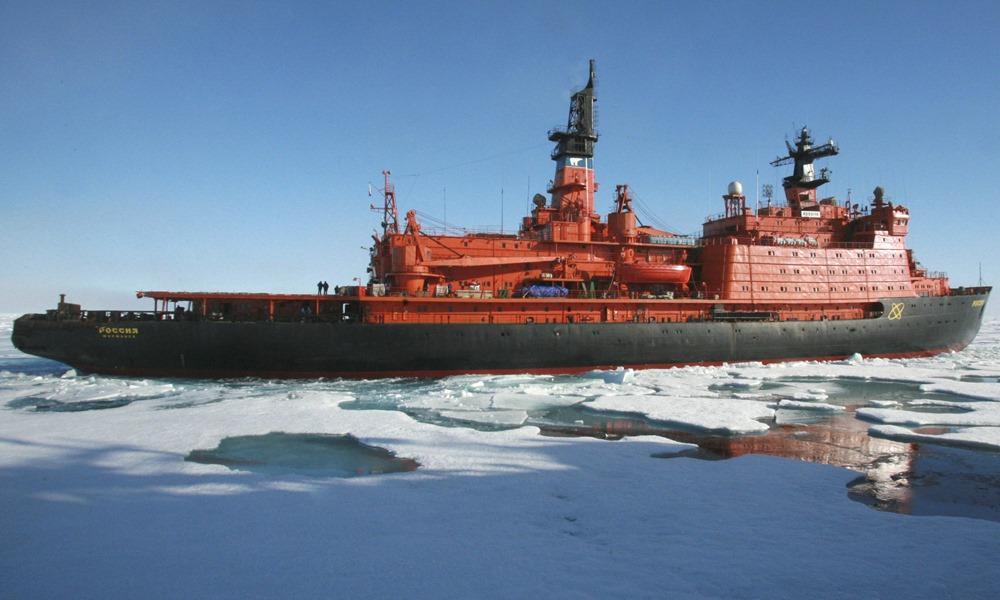

In the Summer of 1990, this nuclear ship was used to transport an expedition of 40 West Germans to the North Pole. This was the first non-communist charter of a nuclear icebreaker. The ship operated in the Gulf of Finland during winter 2012-13.
Rossiya's itinerary program offered North Pole expeditions and also longer voyages on the Northern Sea Route (along Russia's Arctic coastline). Russia's nuclear fleet of ice-breaking vessels is used exclusively in the Arctic Ocean for escorting merchant ships and assisting research stations floating in the ice-covered waters north of Siberia. These ships are also used for scientific and Arctic cruise expeditions. The Russian nuclear ice-breakers must sail in ice-cold waters to effectively cool their reactors.
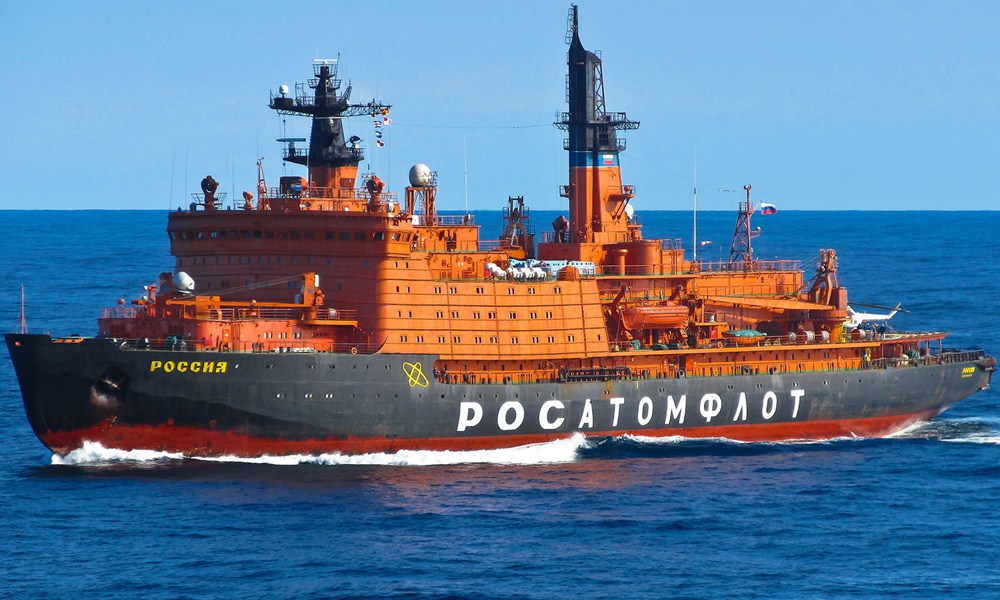

NS Rossiya belongs to the Arktika-class (Project 10520) nuclear ships - until 2017 the world's largest and most powerful ever constructed. The ship is one of all 6 units in this class (Arktika-class/Project 10520), together with the old Sibir (1977-1992), the old Arktika (1975-2008), Sovetskiy Soyuz (1990), Yamal (1992), and 50 Let Pobedy (2007).
All units were constructed at Baltiysky Zavod/Baltic Shipyard (Sankt-Petersburg).
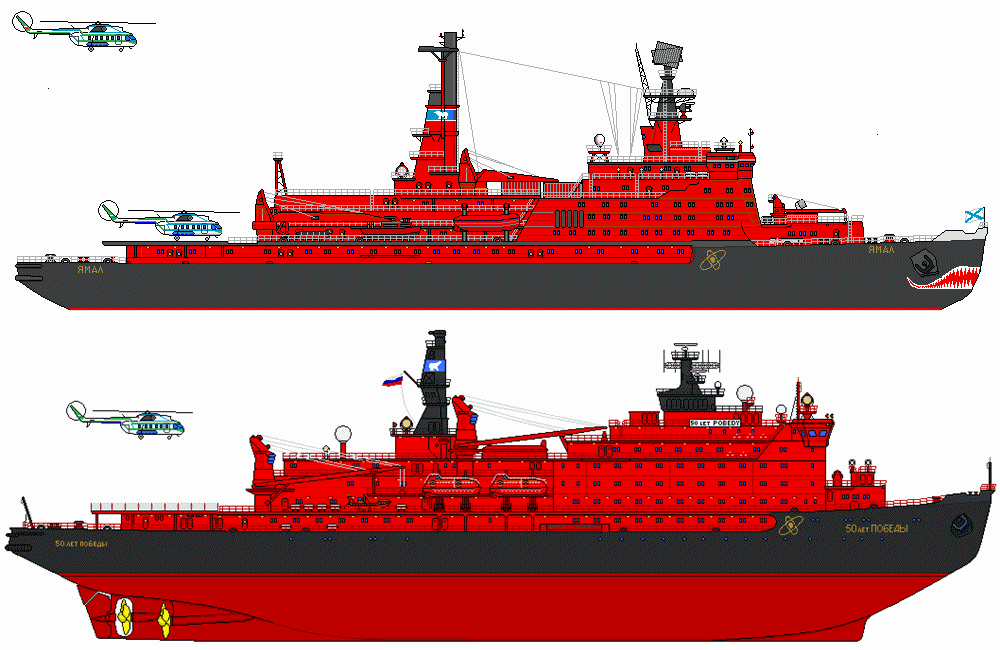
The vessel has 1 dining room, Sauna, Library, Auditorium, Passenger Lounge, Gymnasium, 1 swimming pool (indoor, heated), Infirmary, 1 elevator, 1 helipad (helicopter deck) with 2 helicopters.
- LOA Length: 150 m / 492 ft
- Beam/width: 30 m / 98 ft
- GT-tonnage: 20680 tons
- Decks: 5 (2 with cabins)
- Crew: 140
- Passengers: 100
- Max Speed: 21 knots / 39 kph / 24 mph
- Max Draught: 11 m (36 ft)
- DWT Deadweight tonnage: 2713 tons
- Displacement tonnage: 23630 tons
- Icebreaking capacity: 2,8 m (9 ft)
- Range: unlimited (4 years endurance)
- Powerplant: two OK-900A nuclear reactors (each 171 MW, or combined 342 MW power output)
- Propulsion: turbo-electric, 3 shafts, 3 electric motors (17,6 MW output each, or 52,8 MW combined power output).



