Aleksandr Sannikov icebreaker
Former name : Alexander Sannikov
Aleksandr Sannikov icebreaker current position
The current location of Aleksandr Sannikov icebreaker is in North Russia cruising en route to RU SAB. The AIS position was last reported 21 minutes ago.
Current PositionSpecifications of Aleksandr Sannikov icebreaker
| Year of build | 2018 / Age: 8 |
| Flag state | Russia |
| Builder | Vyborg Shipyard PJSC (Vyborg, Russia) |
| Class | Aker Arctic ARC130A (Icebreaking Support Vessel) |
| Building cost | EUR 230 million (USD 270 million) |
| Engines (power) | Wartsila (27 MW / 36208 hp) |
| Propulsion power | 21.5 MW / 28832 hp |
| Speed | 16 kn / 30 km/h / 18 mph |
| Length (LOA) | 122 m / 400 ft |
| Beam (width) | 26 m / 85 ft |
| Gross Tonnage | 11295 gt |
| Beds | 35 |
| Decks | 6 |
| Decks with cabins | 2 |
| Sister-ships | Andrey Vilkitsky |
| Former names | Alexander Sannikov |
| Owner | Gazprom Neft (Russia) |
| Operator | LLC Gazprom Neft Novy Port |
Aleksandr Sannikov icebreaker Review
Review of Aleksandr Sannikov icebreaker
MS Aleksandr Sannikov ("ледокол Александр Санников") is an icebreaking vessel owned and operated by Gazprom Neft ("Газпром нефть"). The shipowner is a Russian state-owned corporation (a subsidiary of PAO Gazprom) specializing in oil production and shipping. Gazprom Neft is headquartered in Sankt-Petersburg and is Russia's third-largest oil producer.
The vessel (IMO number 9777101) is Russia-flagged (MMSI 273394350) and registered in Sankt-Petersburg.
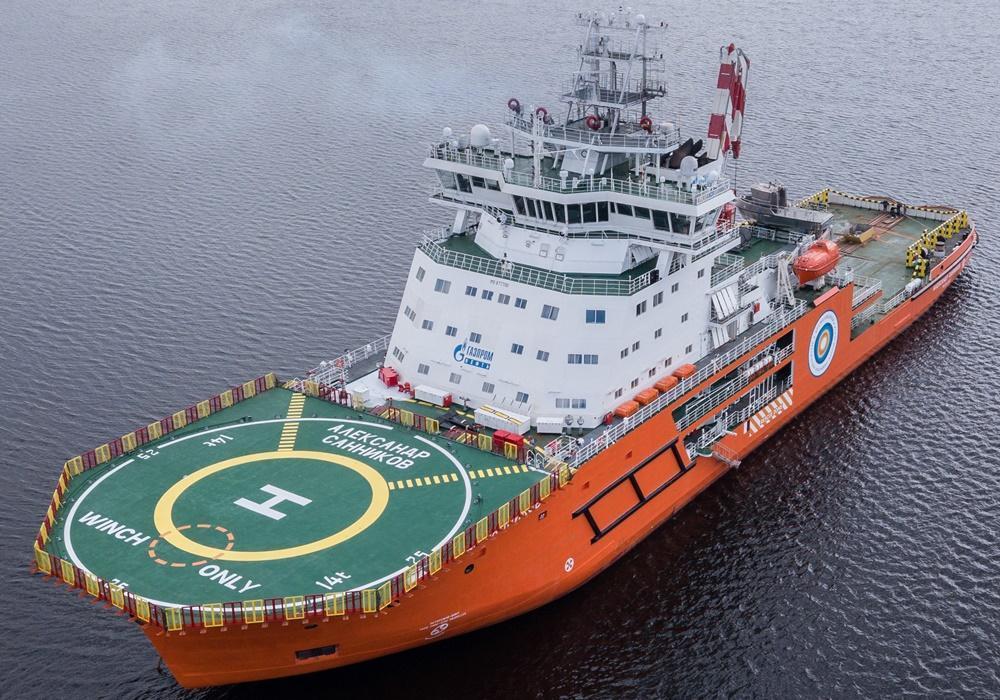

Both sisterships (Sannikov and Vilkitsky) are deployed in Ob Bay (Yamal Peninsula, Arctic Russia) to support Gazprom's Arctic Gate (Novy Port offshore crude-oil loading terminal of the Novoportovskoye oil field). Their duties include escorting and assisting oil and LNG tankers operating along Russia's Northern Sea Route, which connects Asia with Northern Europe.
These icebreakers provide mooring and tug assistance, conduct cargo loading and rescue operations, and support firefighting and oil spill response efforts. Gas tankers operate between Port Sabetta (Yamal LNG plant) and Kamenny Cape (Ob Bay), while oil tankers are escorted to the Novy Port terminal (featuring sea mooring), where they receive support during berthing and loading operations.
Alexander Sannikov Vessel Details
In 2014, Gazprom Neft signed a contract with Aker Arctic (Finland) to develop a conceptual vessel design based on Aker's ARC130 supply icebreaker, originally developed for the Finnish Transport Agency (FTA). The new ship design, ARC130A ("A" stands for "Arctic"), is an enlarged version of the ARC130 model used for the Polaris icebreaker.
The ARC130A variant includes enhanced ice-strengthening, greater propulsion power (total output of 21.5 MW, compared to 19 MW on Polaris), improved dynamic positioning, and additional equipment for towing, firefighting, and oil spill response. Unlike Polaris, which operates on both LNG (Liquefied Natural Gas) and LSMDO (Low Sulfur Marine Diesel Oil), ARC130A icebreakers use only LSMDO.
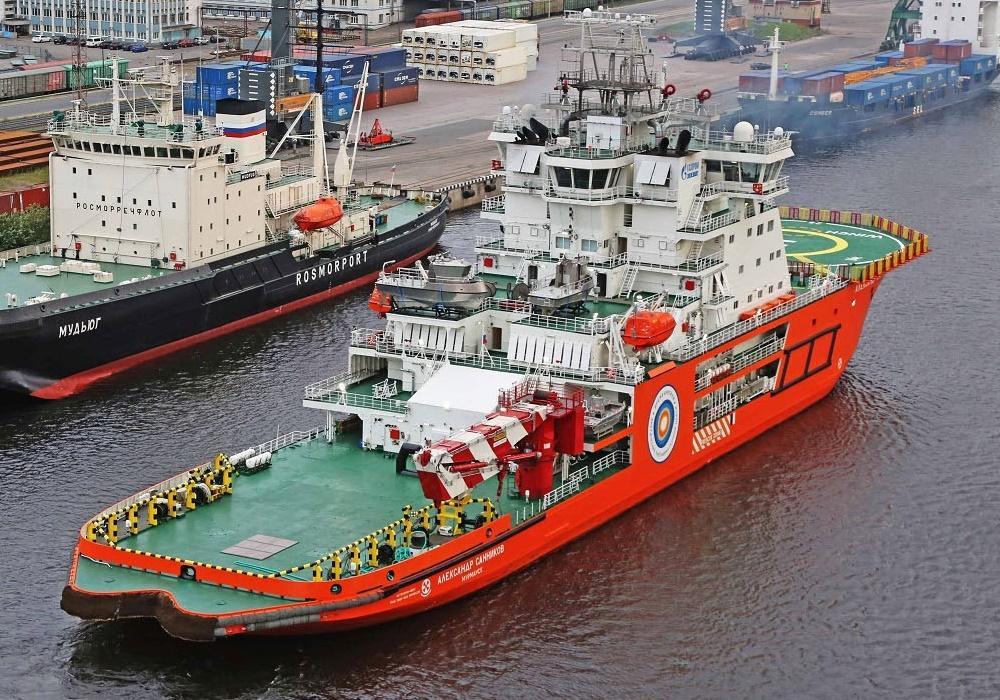

The ARC130A model was validated in August 2015 following successful open-water and ice trials at Aker Arctic's test lab in Helsinki (Finland). The shipbuilding contract between Gazprom Neft and Vyborg Shipyard was signed the same year and covered the construction of two vessels. The first ship, Sannikov, was delivered in June 2018, followed by Vilkitsky in December 2018. The icebreaker's projected service life is 50 years.
The ship features a double-bottom hull with structural reinforcements in critical areas, advanced DP2 (Dynamic Positioning Class 2) and maneuvering systems, state-of-the-art radio navigation equipment, remote electronic control, an autopilot system, and an advanced automatic powerplant management system capable of operating independently for several days.
Compared to Russia's nuclear-powered icebreakers, the ARC130A design offers greater maneuverability, lower fuel consumption, and significantly reduced construction and maintenance costs. The uniquely shaped hull allows for 360-degree turns in ice within just one minute.
In addition to icebreaking, the vessel can carry containerized cargo (up to 8 TEUs) on a dedicated deck and accommodate up to 35 personnel. The aft deck crane has a 25-ton lifting capacity and a reach of 27 meters. The foredeck features a helipad (helideck) rated for 14 tons, suitable for one Mi-8 helicopter (a medium-sized twin-turbine model). Onboard medical facilities include an infirmary, treatment room, and quarantine cabin. The ship also features a mess hall (dining room and lounge) and a sauna. For oil spill response, stern-mounted brush skimmers and recovery equipment (containers and tanks) are installed, with a total capacity of 1300 m³ (46,000 ft³).
The vessel is designed for year-round operations in thick first-year ice and is classified as "Icebreaker 8" by the Russian Maritime Register of Shipping, indicating it is capable of escorting vessels in severe ice conditions. Its icebreaking capacity is 2 meters (6.5 feet) of pack ice at 2 knots (1 mps) in both forward and reverse. In brash ice, the capacity increases to 7 meters (23 feet) at 4 knots (2 mps) in both directions.
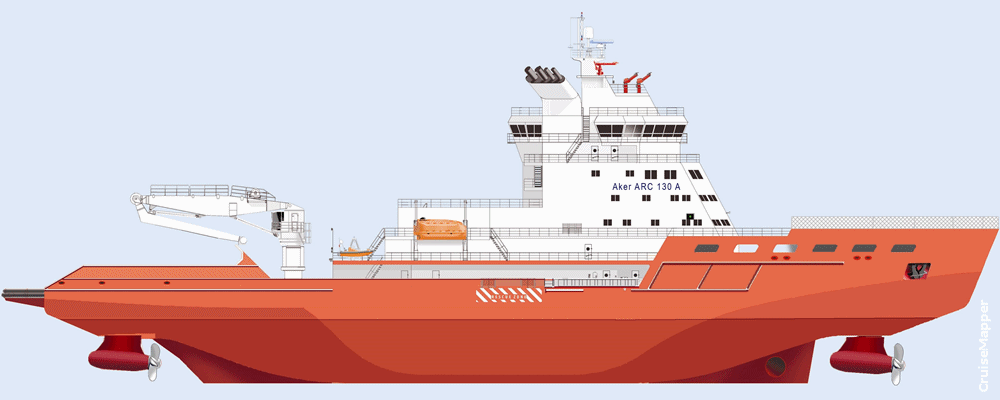
The midship-located powerplant (main deck level) comprises two pairs of Wartsila generator sets (medium-speed engines) with exhaust gas economizers. An auxiliary harbor generator (1.2 MW output) supplies electricity while docked. The powerplant includes four Wartsila diesel-electric generator sets (two 8L32E and two 16V32E engines, combined output 27 MW) and one emergency generator. The vessel’s endurance for fuel and supplies is 30 days.
The ABB diesel-electric propulsion system features three azipods (ABB Azipod motors/azimuth thrusters) with fixed-pitch propellers. Two azipods are located at the stern (combined output 21.5 MW), and one is at the bow (output 1.8 MW).
Note: In areas with limited AIS coverage, tracking the vessel's real-time location may not be possible. Visit CruiseMapper's Icebreakers hub for a complete list of icebreakers and icebreaking research ships, organized by country and fleet.
Other Gazprom Russia cruise ships
Aleksandr Sannikov icebreaker Wiki
Vessel construction began on November 3, 2015. The ship was launched on November 24, 2016, and delivered to Gazprom Neft on June 29, 2018. Sea trials were conducted in the Gulf of Finland.
The christening ceremony took place on June 29, 2018, at Angliyskaya Naberezhnaya in St. Petersburg and was followed by a farewell show. The event was attended by Vadim Yakovlev (First Deputy CEO of Gazprom Neft), Aleksey Rakhmanov (President of United Shipbuilding Corporation), and Aleksandr Solovyov (General Director of Vyborg Shipyard).
The shipbuilder, Vyborg Shipyard PJSC (founded in 1948), specializes in building icebreakers, offshore support vessels, semi-submersible drilling and oil production platforms, and fishing trawlers. The yard has extensive production facilities—64,000 m² indoors and 18,500 m² outdoors—and can construct vessels with a maximum deadweight (DWT) of 15,000 tons. For large shipbuilding projects, hulls are pre-assembled on the yard’s semi-submersible barge, Atlant. Since 2012, Vyborg Shipyard has been fully owned by United Shipbuilding Corporation (OCK), a state-owned Russian company that also jointly owns Arctech Helsinki Shipyard (50%) alongside Meyer Turku Oy (50%).
Other newly built Russian icebreaking support and supply vessels include SCF Sovcomflot’s Vitus Bering (2012), Aleksey Chirikov (2013), Fedor Ushakov (2017), Gennadiy Nevelskoy (2017), Stepan Makarov (2017), and Yevgeny Primakov (2018). These icebreakers support operations at Russia’s Sakhalin-1 oil field in the Sea of Okhotsk, offshore Sakhalin Island.