Yamal icebreaker
Yamal icebreaker current position
The current location of Yamal icebreaker is in North Russia cruising en route to ARCTIC. The AIS position was last reported 28 minutes ago.
Current PositionSpecifications of Yamal icebreaker
| Year of build | 1992 / Age: 34 |
| Flag state | Russia |
| Builder | Baltiysky Zavod/Baltic Shipyard (St Petersburg, Russia) |
| Class | Russian nuclear icebreaker (Arktika-class, Project 10520) |
| Engines (power) | OK-900A nuclear reactors (342 MW / 458630 hp) |
| Propulsion power | 52.8 MW / 70806 hp |
| Speed | 22 kn / 41 km/h / 25 mph |
| Length (LOA) | 150 m / 492 ft |
| Beam (width) | 30 m / 98 ft |
| Gross Tonnage | 20646 gt |
| Passengers | 100 |
| Crew | 150 |
| Decks | 8 |
| Cabins | 50 |
| Decks with cabins | 4 |
| Sister-ships | Arktika (1975), Sibir (1977), Rossiya (1985), Sovetskiy Soyuz (1990), 50 Let Pobedy (2007) |
| Owner | Russian Federation (via FSUE Atomflot) |
| Operator | Rosatom (Rosmorport) |
Yamal icebreaker Review
Review of Yamal icebreaker
NS Yamal ("атомный ледокол Ямал") is Russian nuclear icebreaker. "NS" stands for "nuclear ship". The vessel is state-owned (by the Russian Federation via FSUE Atomflot) and operated by Rosatom. The Atomflot company provides all Russian nuclear icebreakers with maintenance and technological services. The company also serves the country's special vessels fleet.
The vessel (IMO number 9077549) is Russia-flagged (MMSI 273132400) and registered in Murmansk.
The list of other Russian icebreaker cruise ships also includes Akademik Ioffe, Akademik Sergey Vavilov, Kapitan Dranitsyn, Kapitan Khlebnikov, 50 Let Pobedy.
Besides NS Yamal, the list of other active Russian nuclear icebreaker ships includes Taymyr (1989), Vaygach (1990), 50 Let Pobedy (2007), Arktika (2020), Sibir (2021), Ural (2022), Yakutia (2024), Chukotka (2026), Rossiya (2027/Project Leader), Sevmorput (1988, cargo ship).
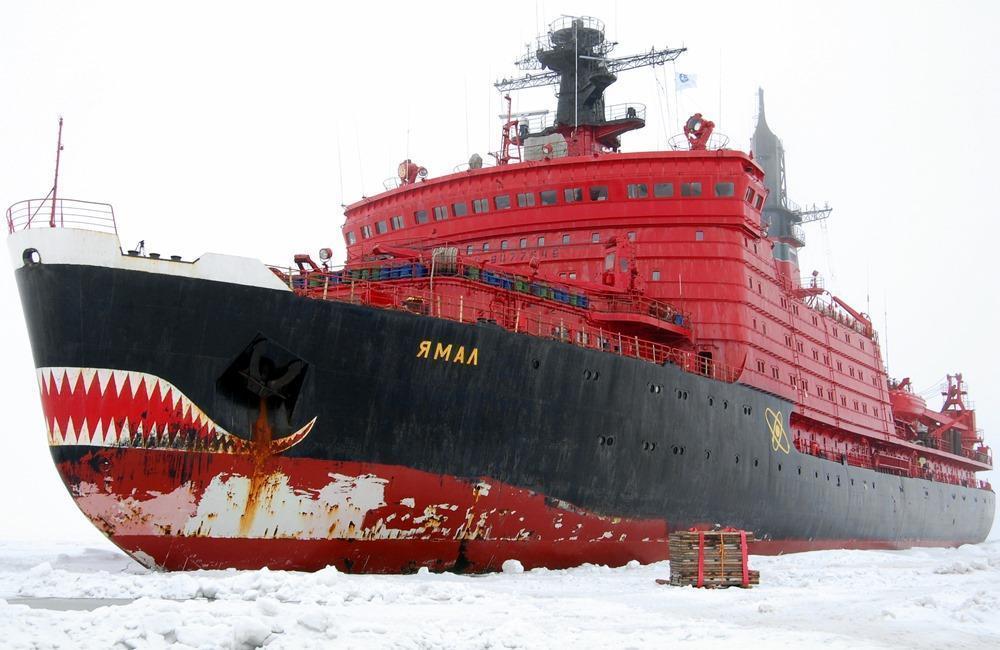

One of the Russian icebreaker cruise ships, Yamal is a nuclear-powered icebreaking vessel of the Arktika-class. It is named after the Yamal Peninsula (Northwest Siberia). The name's meaning is "End of the Nenets Land". Nenets (aka Samoyeds) are indigenous people living in the arctic regions of Russia. NS Yamal was laid down in Leningrad in 1986, but launched 6 years later - in October 1992, after the breakup of USSR (the Soviet Union). This nuclear ship never filled its designed role - to keep the Arctic shipping route open. Instead, it has always carried passengers on Arctic "icebreaker" cruises. In July 1994, Yamal took an excursion to the North Pole with the National Science Foundation (NSF) to celebrate ship's Official Maiden Voyage. While at the exact north pole, the cruise passengers and the crew celebrated with a barbecue at -10 degrees F temperature (wind gusts measured at -40 degrees F). Because of the 90/90 coordinates, the Captain (Smirnov) organized a swimming party with Mr. Will Rountree - a US citizen. The American was recorded as the first person to ever swim there (July 21, 1994). Water temperature was below freezing, ~30 degrees F. Yamal played a significant role in the creation of North Pole annual cruise travel expeditions, being one of the few ships capable to get there and bring tourists in safety. Since 1993, the ship is operated by the Murmansk Shipping Company (abbrev MSCO) with operations in Arctic Russia and also in Baltic Sea (northern Europe). During 2001-2008 period, the ship was also operated by Poseidon Expeditions (the Arctic and Antarctica cruise operator).
Among the most serious NS Yamal ship accidents are:
- December 23, 1996 - a crew member was killed when a fire broke out on the ship. The fire was extinguished within 30 min. The nuclear reactor was not affected.
- March 16, 2009 - the ship collided with MT Indiga (Russia-flagged product tanker/oil tanker). The accident occurred in Kara Sea (Yenisei Gulf, the Yenisei River's estuary). The oil tanker suffered a 9,5 m (31 ft) crack on its main deck. No damage was reported for the ice-breaker.
The icebreaker's itinerary program offers North Pole expedition cruises and also longer itineraries on the Northern Sea Route along Russia's Arctic coastline. Russia's nuclear fleet of ice-breaking vessels is used exclusively in the Arctic Ocean for escorting merchant ships and assisting research stations floating in the ice-covered waters north of Siberia. These ships are also used for scientific and Arctic cruise expeditions. The Russian nuclear ice-breakers must sail in ice-cold waters to effectively cool their reactors.
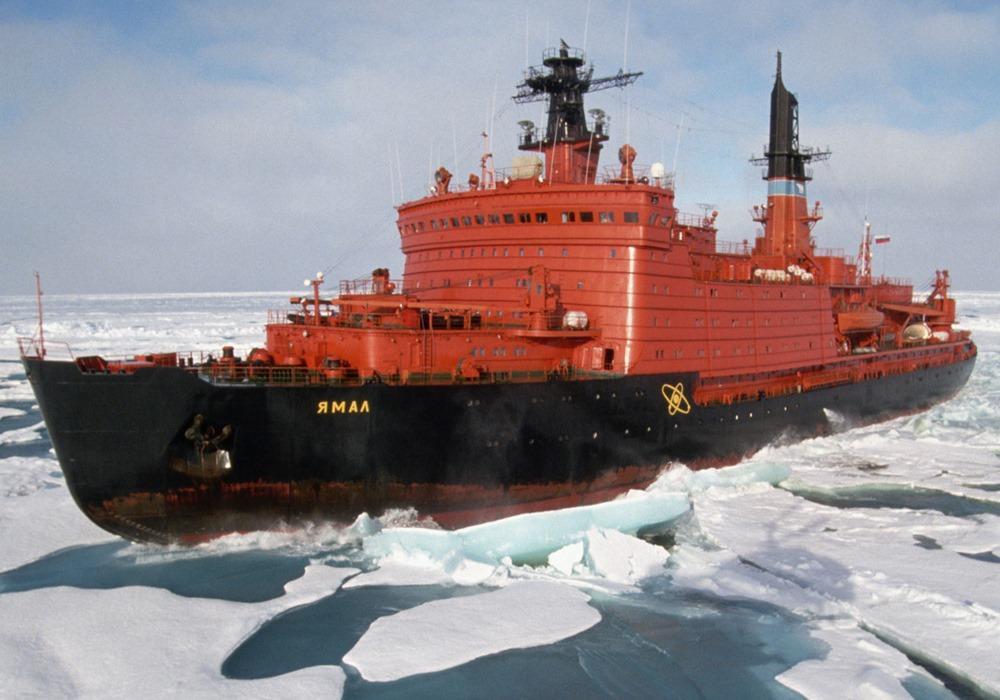

NS Yamal vessel details
Yamal is one of all 6 icebreaking vessels of the Arktika class - together with the old Sibir (1977-1992), the old Arktika (1975-2008), Rossiya (1985-2013), Sovetskiy Soyuz (1990) and 50 Let Pobedy (2007).
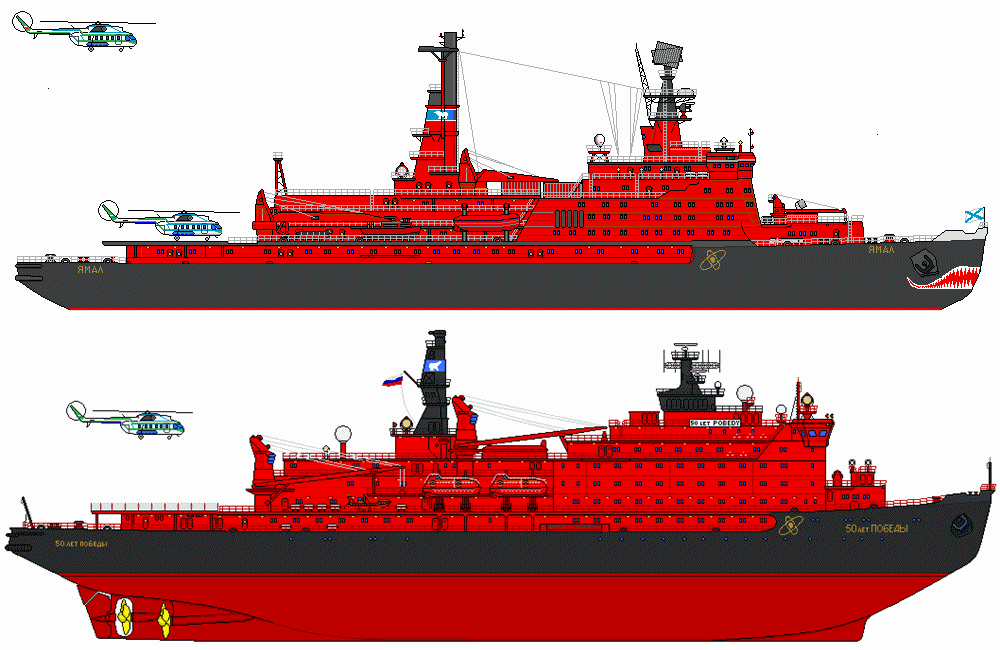
The vessel has 1 dining room, Sauna, Library, Auditorium, Passenger Lounge, Volleyball Court, Gymnasium, 1 swimming pool (indoor, heated), Infirmary, 1 elevator, 1 helipad (helicopter deck) with a Mi-2 transport helicopter. The ship is also equipped with Zodiacs (large-capacity inflatable boats) used for remote landings.
- DWT Deadweight tonnage: 2750 tons
- Displacement tonnage: 23455 tons
- Max Draft: 11 m (35 ft)
- Icebreaking capacity: 5 m (16 ft)
- Ice-class LL1
- Range: unlimited (4 years endurance)
- Powerplant: 2x OK-900A nuclear reactors (each 171 MW, or combined 342 MW power output)
- Propulsion: turbo-electric, 3 shafts, 3 electric motors (17,6 MW output each, or 52,8 MW combined power output).
Note: In the case of poor AIS coverage, tracking the vessel's current location will be impossible. You can see CruiseMapper's list of all icebreakers and ice-breaking research ships in the "itinerary" section of our Icebreakers hub. All states and their fleets are listed there.

