Ferries
History, Review, Itineraries, Ships, Deck Plans, News
Ferries fleet
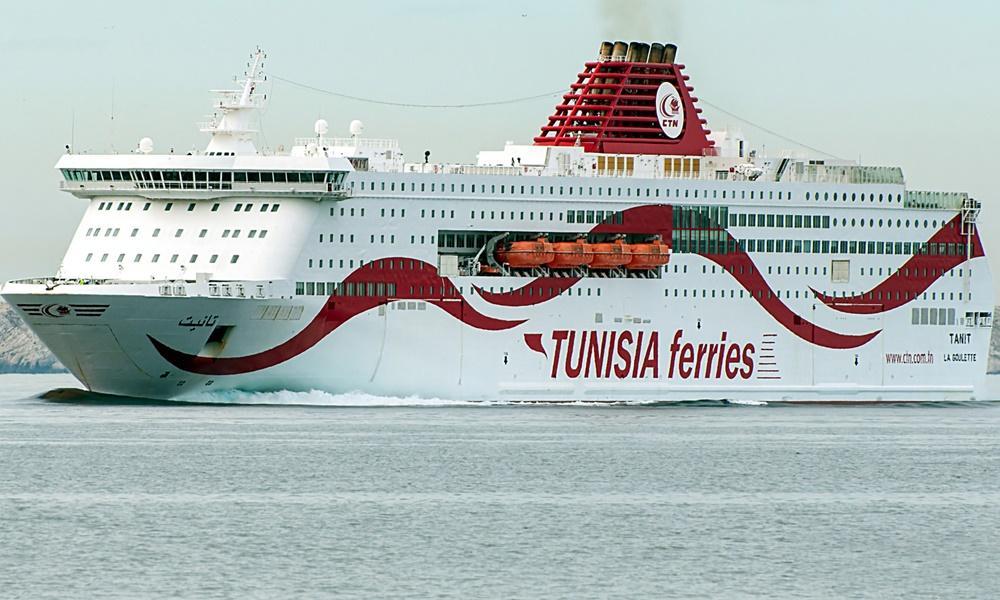

CTN Tanit ferry
Routes: Genoa-La Goulette (Tunis)-MarseilleCOTUNAVYear build 2012 / Age : 14 Passengers 3200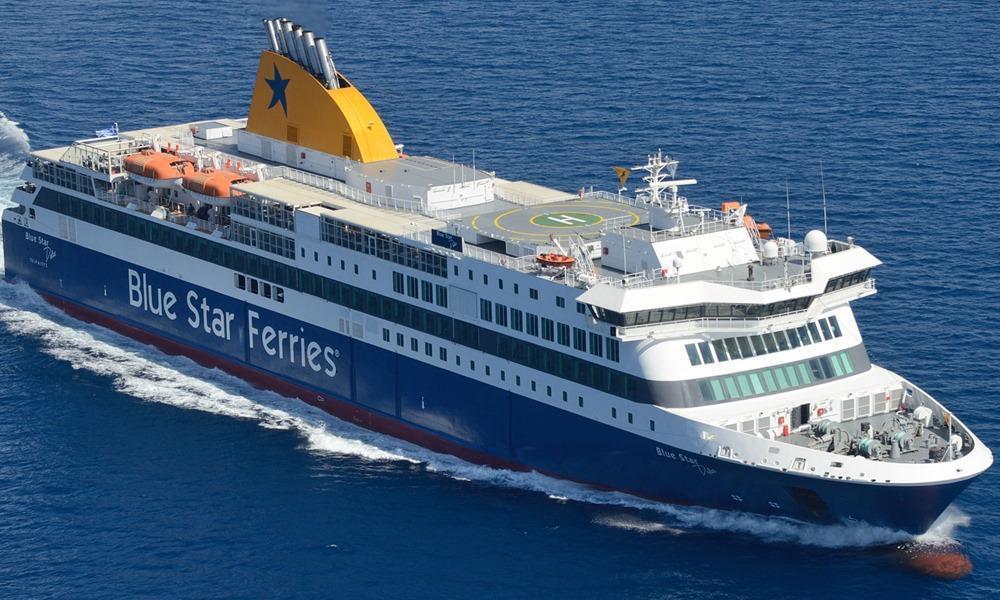 
Blue Star Patmos ferry
Routes: Piraeus-Kalymnos-Kos-Rhodes, Astypalaia-Patmos-Leipsoi-Leros-Nisyros-Symi-Tilos-KastellorizoBLUE STAR FERRIESYear build 2012 / Age : 14 Passengers 2400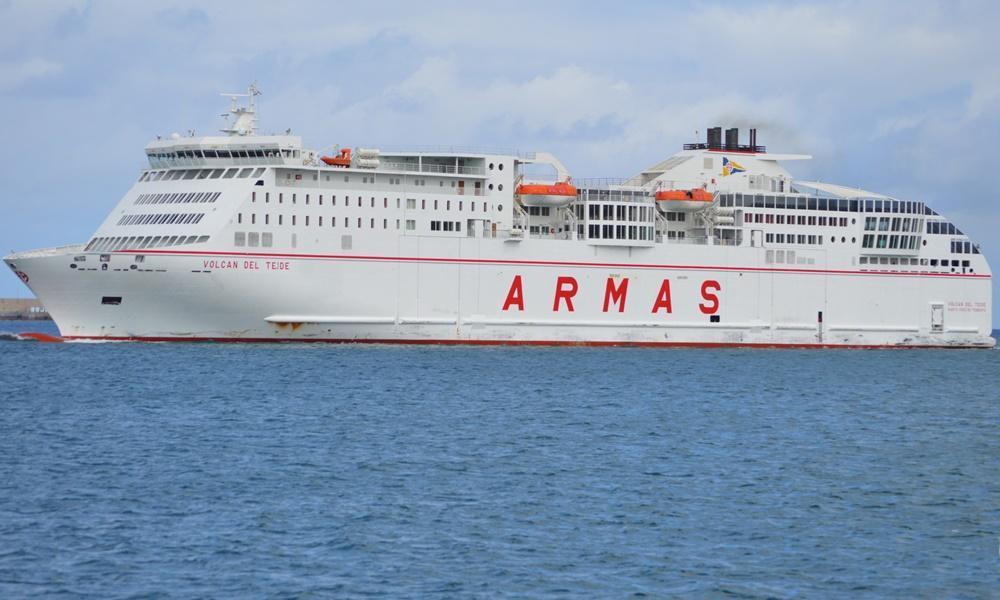 
Volcan del Teide ferry
Routes: Las Palmas (Gran Canaria)-Santa Cruz (Tenerife)-Huelva (Spain)NAVIERA ARMASYear build 2011 / Age : 15 Passengers 1500 
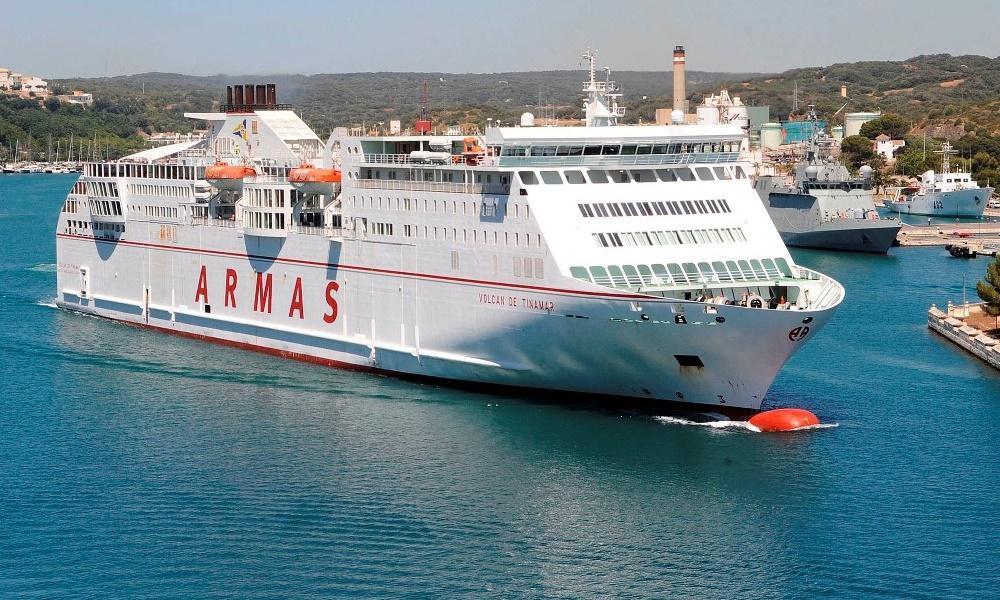

Volcan de Tinamar ferry
Routes: Las Palmas (Gran Canaria)-Santa Cruz (Tenerife)-Huelva (Spain)NAVIERA ARMASYear build 2011 / Age : 15 Passengers 1500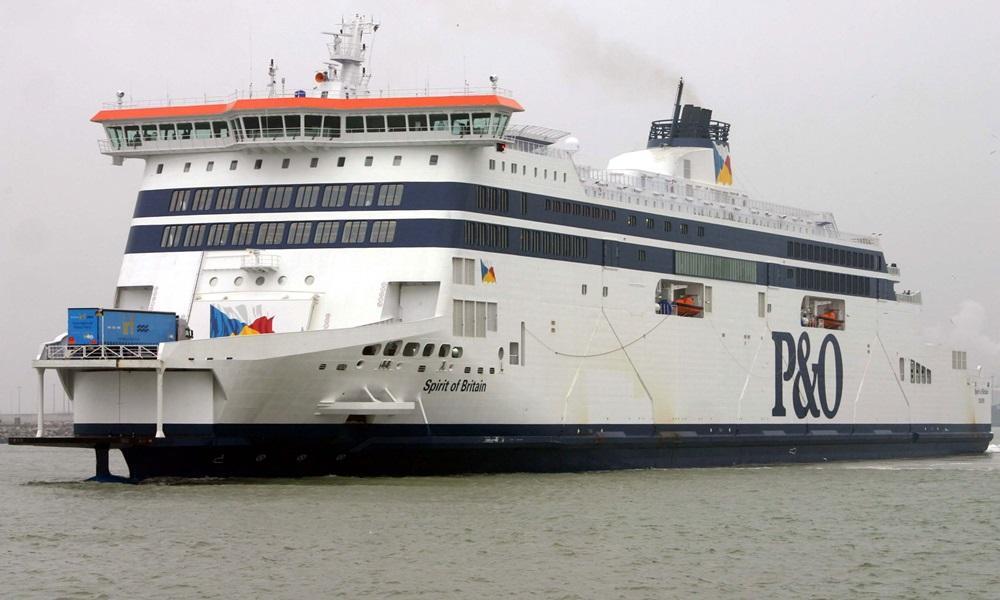 
Spirit of Britain ferry
Routes: English Channel (Dover-Calais)P&O FERRIESYear build 2011 / Age : 15 Passengers 1750 - 2000 
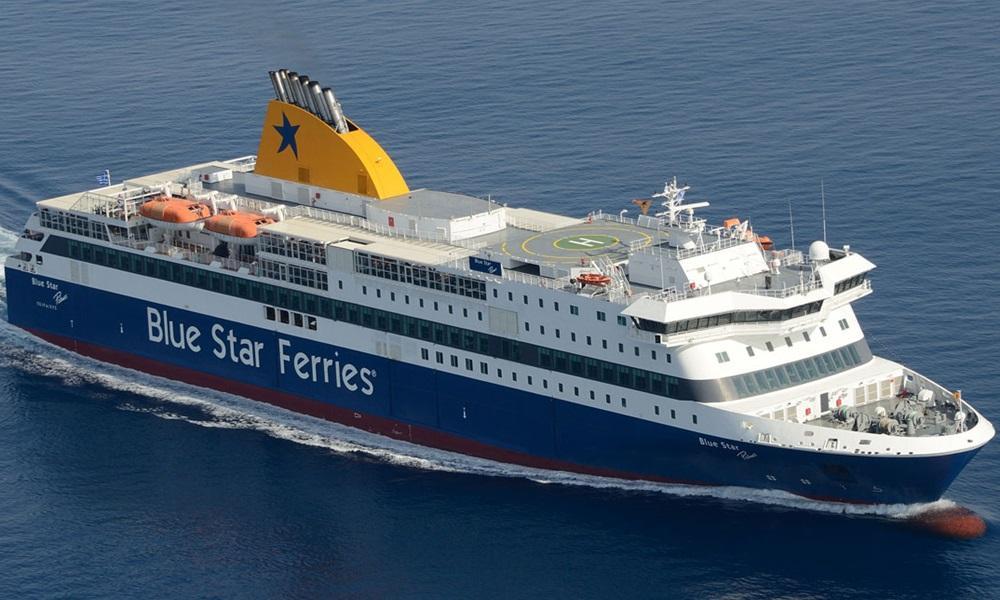

Blue Star Delos ferry
Routes: Piraeus-Syros-Paros-Naxos-Ios-Santorini-AnafiBLUE STAR FERRIESYear build 2011 / Age : 15 Passengers 2400 
Stena Hollandica ferry
Routes: Harwich-Hook of HollandSTENA LINEYear build 2010 / Age : 16 Passengers 1200 
Stena Britannica ferry
Routes: Harwich-Hook of HollandSTENA LINEYear build 2010 / Age : 16 Passengers 1200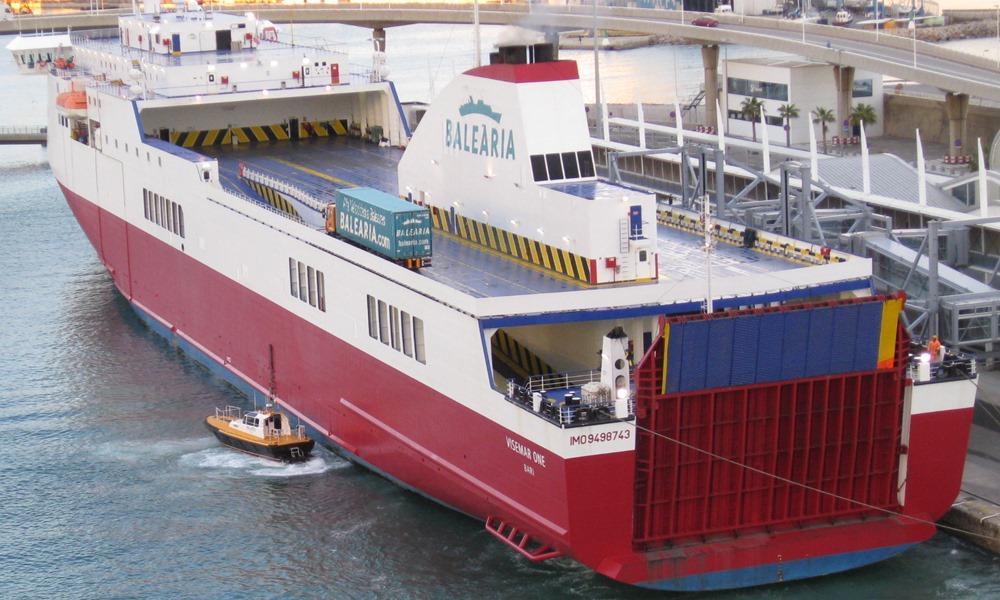 
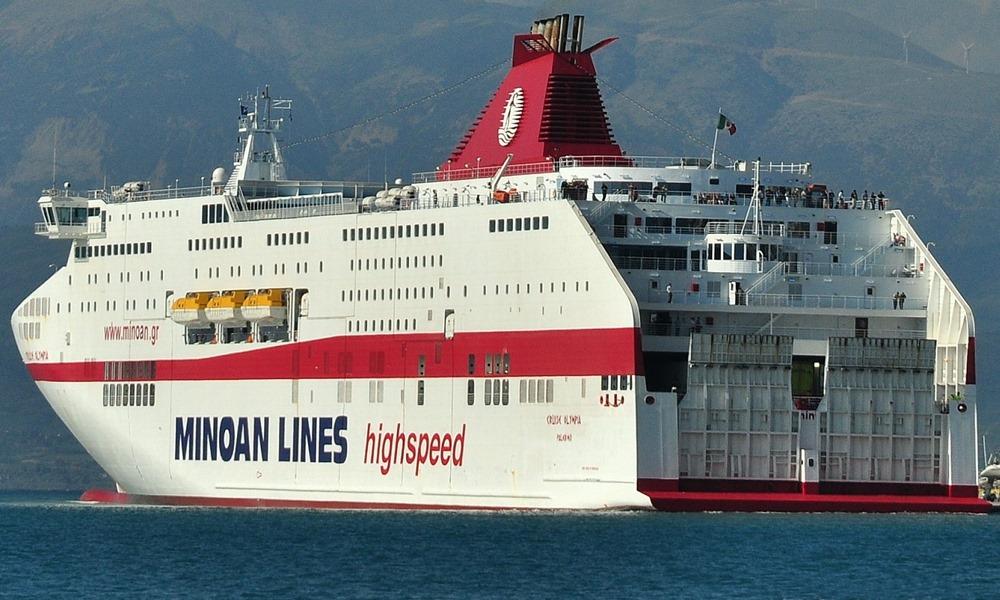

Cruise Olympia ferry
Routes: Patras-Igoumentisa-Ancona-TriesteMINOAN LINESYear build 2010 / Age : 16 Passengers 2850 
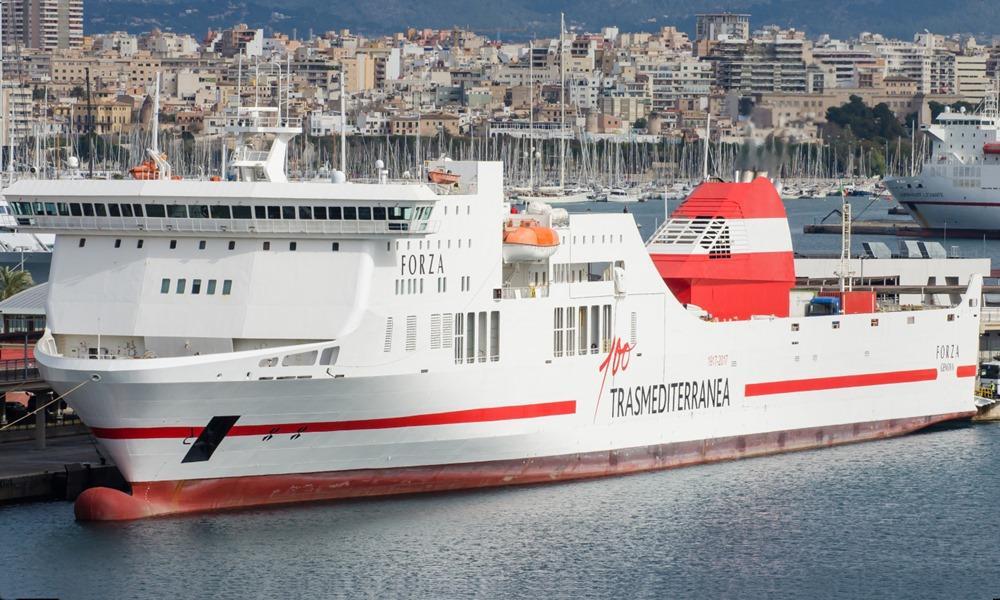

Forza ferry
Routes: Ancona-Igoumenitsa-(Patras), Bari-Igoumenitsa-(Patras), Venice-IgoumenitsaTRASMEDITERRANEAYear build 2010 / Age : 16 Passengers 969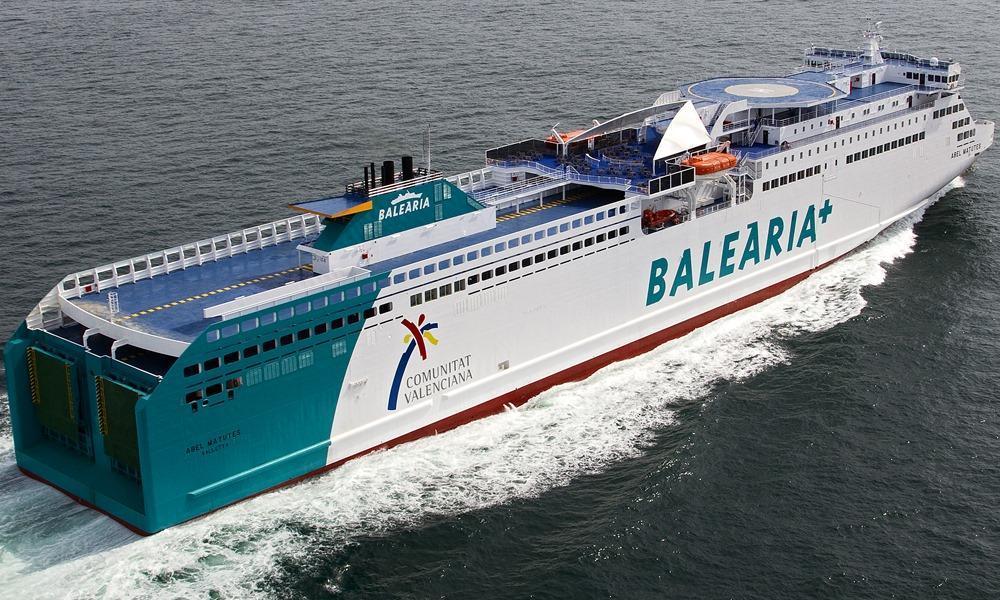 
Abel Matutes ferry
Routes: Barcelona-Palma de Mallorca, Valencia-Ibiza-Palma de Mallorca, Huelva-CanariasBALEARIAYear build 2010 / Age : 16 Passengers 900
Review of Ferries
This is CruiseMapper's hub listing all the world's newest and largest cruise ferry ships. Our list of passenger ferries includes vessels operated by the world's largest ferry companies. The links below are internal and redirect to each company's review here. The "routes" and "fleet" links (in brackets by brand) are also internal and show the company's vessels and services (homeports/crossing times).
- VIKING LINE, STENA LINE, TALLINK-SILJA LINE, FINNLINES, TT LINE
- DFDS SEAWAYS, P&O FERRIES, BRITTANY FERRIES, IRISH FERRIES
- COLOR LINE, BALEARIA, MOBY LINES, GRIMALDI LINES
- GNV (Grandi Navi Veloci), TIRRENIA, SNCM (Maritima Ferries)
- TRASMEDITERRANEA, CORSICA-SARDINIA FERRIES, CORSICA linea, NAVIERA ARMAS (Canary Islands)
- MINOAN LINES, HELLENIC SEAWAYS, BLUE STAR FERRIES, SUPERFAST FERRIES, SEAJETS FERRIES GREECE
- ANEK LINES, NEL LINES
- BC FERRIES
- Norwegian ferries (COLOR LINE, FJORD LINE, FJORD1 LINE, Hurtigruten, Havila Voyages)
- MOL FERRIES (Japan)
- plus small-fleet companies - DESTINATION GOTLAND, CONDOR FERRIES, POLFERRIES, NORTHLINK FERRIES (Scotland), MARINE ATLANTIC, ECKERO LINE, TT-LINE Tasmania
The Greek company Attica Holdings SA (also known as Attica Group, 1918-founded) fully owns as subsidiaries SUPERFAST FERRIES, BLUE STAR FERRIES, HELLENIC SEAWAYS (since 2018), and AML-AFRICA MOROCCO LINK (2016-founded). As of 2021, Attica Group owns and operates 32 vessels connecting 71 ports/islands in 4 countries, with annual volumes of over 7 million passengers, approximately 1 million passenger vehicles, and around 400,000 trucks.
Based on FY2016 data, the largest European ferry companies (by fleet tonnage, berths, and annual revenue) were ranked as follows:
| Company | Fleet GT (gross tons) | Fleet Beds | Revenue (EUR) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stena Line | 909,412 | 16,847 | 1.335 billion |
| Grimaldi Lines | 477,667 | - | - |
| Tallink | 466,960 | 18,963 | 945 million |
| DFDS Seaways | 412,722 | - | 1.805 billion |
| P&O Ferries | 409,659 | - | - |
| Viking Line | - | 14,026 | 530 million |
| GNV | - | 13,328 | - |
| Tirrenia | - | 11,876 | - |
| Finnlines | - | - | 511 million |
Ro-Ro Ships
RoRo vessels (roll-on / roll-off) can include ferries, cruise ferries (with passenger cabins), cargo ships, and freight barges. RoRo ships used exclusively for vehicle transportation (cars and trucks) are categorized as PCC ("Pure Car Carriers") and PCTC ("Pure Truck and Car Carriers").
ROPAX ("roll-on / roll-off passenger") is a RoRo ship built for vehicle transport and passenger staterooms (inside and outside). RoRo vessels with a capacity of 500+ passengers are categorized as "cruise ferries".
Unlike other cargoes measured in metric tons, ro-ro cargoes are wheeled and measured in lane meters (LIMs). LIMs per ship is calculated by multiplying the vehicle length (in meters) by the number of cargo decks and by the width in lanes (which differs from ship to ship). The most common types of wheeled cargoes on ferries are automobiles, lorries, semi-trailer trucks, trailers, and railroad cars. These vehicles are driven on/off the ferry on their own wheels, and some use a platform vehicle (tug master).

Some vessels are owned by one company and operated under time charter by another. Often, during the ship charter period, the vessel's name is changed.
Ferry Types
The legal definition of a ferry is a continuation (prolongation) of a road over a navigable waterway. Ferries as vessels can be categorized as:
- Fast-speed catamaran ferries are generally operated as passenger ships, but the largest of them also carry cars. The most famous catamaran ferry services are in the UK.
- Car ferries are wheeled cargo ships operating on short routes between islands and the mainland. In the USA, car ferries can also carry railway carts.
- RoRo ferries are mainly used in the UK. Most of them are ROPAX ships, and larger vessels are advertised as "cruise ferries" with dedicated bar and seating lounges, as well as passenger cabins.
Double-ended ferry design allows vehicles to be loaded/unloaded via the ship's both ends (bow and stern). Currently, the world's largest double-ended passenger ferries are owned by BC FERRIES. The Coastal-class sisterships Coastal Celebration, Coastal Inspiration, and Coastal Renaissance were all built in Flensburg, Germany. Double-ended ferries are used mainly on short routes (including river crossings) as they save maneuvering time, lower fuel consumption (and risks) before docking. A unique feature of such ships is the doubled propulsion (identical units installed at each end). This results in better stopping power and greater maneuverability compared to standard ferries.
All RoRo ships have built-in vehicle ramps allowing wheeled cargo to be rolled on and off the ship when docked in port. Generally, the term "RORO vessel" is reserved for larger ships. Their ramps and entry doors are either stern-only (aft) or bow and stern (forward and aft, for quicker loading).
- Currently, the largest cruise ferry in the world by tonnage is Color Magic (2007) with 75,100 GT, a LOA length of 224 m, capacity for 550 cars, and 1,270 lane meters of wheeled cargo (75 trucks).
- Currently, the largest cruise ferry by car capacity is Ulysses (2001) with 50,938 GT, a LOA length of 209 m, capacity for 1,342 cars, and 4,100 lane meters of wheeled cargo (241 trucks).
Domestic ferries in island countries (especially in the Asia-Pacific region) are often the only feasible (affordable) means of transportation. These passenger ships navigate inland waterways, as well as coastal and inter-island routes.
Ferry Terminal
Ferry terminals (also known as Passenger Terminals or Cruise Terminals) are seaport/harbor structures that serve cruise and ferry passengers for embarkation (boarding) and disembarkation (landing). Depending on the port, passenger terminals have from one to several docks (wharves or piers) to berth one or more vessels simultaneously.
Automated Mooring System by Cavotec
In April 2018, it was announced that the engineering company Cavotec (headquartered in Lugano, Switzerland) was contracted to install and maintain its automated mooring system, MoorMaster, at all e-ferry ports in Norway. The project is expected to result in up to a 40% reduction in CO2 emissions, as Norway introduced multiple e-ferries in 2018. These innovative ships are electrically powered and hybrid (running on LNG and batteries). Many of these ferries already use Cavotec's automated charging interface and vacuum-based auto-mooring technology.
MoorMaster eliminates the need for conventional mooring lines to secure the ship at berth (after docking). The system uses remotely controlled and mounted quayside vacuum pads that moor and release the e-ferries in just seconds. This reduces both emissions and noise at the terminal. The smart technology also reduces overall capital expenditure and improves safety in port.
On December 4, 2018, the harbor ferry Suomenlinna 2 (2004-built, 34 m) was successfully remotely piloted in a test area near Helsinki Harbour. The vessel was retrofitted with ABB's Marine Pilot Control (dynamic positioning system) and controlled from Helsinki.
Autodocking System by Wärtsilä
In 2018 (from January to April), the marine engineering corporation Wärtsilä successfully tested its autodocking technology (the world's first). The tests (harbor docking trials) used the Norled-owned hybrid ferry Folgefonn and the Wärtsilä-manufactured wireless charging system.
The autodocking system is activated approximately 2 km from the berth. The vessel continues at normal speed until the full-automatic system gradually slows the ship and activates its docking maneuver until it is secured at the berth. Upon departure, the system can be used in an identical (reverse) manner.
The vessel's maneuvering is automatically controlled by the autodocking system, which manages both steering and propulsion. Manual control is available at any time. Among the benefits for the ship, operators can expect improved safety (reduced likelihood of human errors), less wear and tear (more efficient use of thrusters), and greater efficiency (more time spent at berth).
On December 3, 2018, Rolls-Royce Marine demonstrated the world's first fully autonomous ferry on the Parainen-Nauvo route. In May 2018, Rolls-Royce partnered with Finferries for the SVAN project (Safer Vessel with Autonomous Navigation). For the 400 hours of sea trials (in the Turku Archipelago), the 54-meter-long Falco (a double-ended car ferry) was fitted with numerous sensors and artificial intelligence software. The autonomous cruise ran from Parainen to Nauvo, while the return trip was remotely controlled from Turku (approximately 50 km away). Additionally, Rolls-Royce's autodocking system was also demonstrated.
Cruise Ferries
A cruise ferry is a Ro-Pax passenger vessel that combines a passenger ship with a RoRo vessel ("roll-on / roll-off"). As all cruise ferries have passenger cabins and restaurants, many travelers book them for multi-day "ferry cruises." The ferry's itinerary typically allows only a few hours in port, but you can also stay onboard and never leave the ship until disembarkation day. However, most passengers book ferries as a means of transportation, either within a country or between neighboring countries.
Cruise ferry traffic is primarily concentrated in Northern Europe (Baltic Sea and the North Sea), the English Channel (between the UK and France), the Irish Sea, the Mediterranean (including between Italian and French islands, as well as Europe-North Africa), and the North Atlantic (serving Spain's Canary Islands, Portugal's Azores Islands, Denmark's Faroe Islands, Iceland, and Greenland). Numerous vessels also serve passenger shipping traffic in China, Japan, India, Australia, New Zealand, the USA, and Canada.
Ferries are extremely popular among holiday travelers and private car owners. These ships are among the largest contributors to the growth of vacation tourism in Europe, the USA-Canada, Asia, and Australia-New Zealand.
Ferry Cruise Deals
All cruise ferries offer passenger staterooms that can be booked for overnight stays. Most ships provide wheelchair-accessible cabins (for disabled passengers). Some even have dedicated "pet-friendly cabins" (for pet owners) and are equipped with kennels (located on garage decks or the Sun Deck).
Ferry cruise deals may also include land stays (hotel accommodations or campsite chalets).
Baggage allowance is limited to what passengers can pack in their vehicles.
Passenger cabins are air-conditioned and fitted with en-suite bathrooms. Cabin types include Inside (4-berth, 2-berth) and Outside (2-berth, 3-berth, 4-berth).
Many hotels offer free stays for kids under 12. Onboard children's entertainment programs are often available (usually during peak season), with dedicated supervising staff. The newest and larger ferries have indoor kids' playrooms, arcades, video gaming rooms for teens, and even a swimming pool.
All large cruise ferries feature buffet restaurants, bistros, reserved seating lounges, cocktail bars, patisseries (bakery/coffee shops), boutiques (premium brand shops), elevators (passenger lifts), and sundeck areas.
Golf ferry breaks are also popular, and golf tournament breaks are often offered.
Ferry cruise fares vary based on departure date, route (itinerary, ports), and time (season). Deposits are required to secure peak season bookings. Prices are higher during peak seasons (summer), as well as on weekends and overnight crossings. Early booking usually offers discounted fares.
Follow our concise reviews of the world's largest cruise ferry companies, whose fleets include the world's largest ferries in terms of both size and capacity.
VIKING LINE
Viking Line (routes, fleet, vikingline.com, 1959-founded, Mariehamn, Aland Finland-headquartered) operates on shipping routes connecting Finland, the Åland Islands, Sweden, and Estonia. Viking Line was formed through the merger of three Finnish ferry lines: Rederi Ab Vikinglinjen, Rederi Ab Slite, and SF Line.
From 1970 to 1974, Viking Line became the largest shipping consortium in the Northern Baltic Sea, surpassing Silja Line. During this time, five sister ships were launched by the German shipbuilder Meyer Werft/Papenburg shipyard. In 1973, the line began operations on the Turku-Mariehamn-Stockholm ferry route, directly competing with Silja Line. In 1974, the Helsinki-Stockholm service was established. In 1985, Viking Line launched the world's largest ferry (at the time), MS Mariella, which served the Helsinki-Stockholm route.

In January 2010, Viking Line announced plans to order two 60,000 GT (LNG-powered) vessels for the Turku-Stockholm route to replace the Amorella and Isabella. The newbuilds were expected to feature many cruise-liner standards. The projected deliveries were set for May 2012 and February 2013.
In December 2010, the company signed an official ship order with STX Turku for one 57,000 GT cruise ferry, which was planned for the Turku-Stockholm route. The new ship, Viking Grace, was launched in August 2012 and began operations in January 2013. The second (optional) sister vessel from the series was not ordered.
In November 2016, the company signed a letter of intent with the Xiamen Shipbuilding Yard (China) to build one LNG-powered cruise ferry, Viking Glory (63,000 GT), to replace Amorella. Viking Line did not exercise the option for a second unit under the contract, which expired on January 1, 2018. In August 2022, Amorella was sold to Corsica Ferries.
In 2017, Viking Line ferried 6.88 million passengers. Compared to 2016 (6.50 million), this represented an increase of nearly 6%. This was the highest number in the company's history. The number of ferried cargo units was 127,668, and the number of passenger cars was 762,253 (both all-time records). The greatest increase in passenger shipping volumes was on the Helsinki-Tallinn route, which operated with 12 daily departures during the summer, totaling 2.34 million passengers (a 15.7% increase).
On April 12, 2018, Viking Grace became the world's first passenger ship to use a rotor sail to harness wind power, making it the first hybrid vessel to utilize both wind power and dual-fuel (diesel-gas) engines. The new China-built ferry (still unnamed, scheduled for delivery in 2020) will feature two rotor sails.
In 2019, Viking Line served 6.30 million passengers (compared to 6.41 million in 2018). The Rosella ship alone served 752,336 passengers on the Mariehamn (Åland)-Kapellskär route. Cargo units increased to 133,940 (up from 128,549 in 2018), as did passenger cars, which increased to 714,006 (from 704,799 in 2018). On the Turku-Åland-Stockholm route, 1.80 million passengers were served (down from 1.86 million in 2018), and on the Helsinki-Tallinn route, 1.96 million passengers were served (up from 1.95 million in 2018). The Helsinki-Åland-Stockholm route served 972,000 passengers (compared to 969,000 in 2018).
In "COVID 2020," 1.93 million passengers were served, and this increased to 2.32 million (+20.1%) in 2021. Wheeled cargo traffic in 2021 also grew by 2.9% (129,278 cargo units) and 24% for cars (442,484).
In 2020, 1.93 million passengers were served, and 125,693 cargo units were handled.
STENA LINE
Stena Line (routes, fleet, stenaline.co.uk, 1962-founded, Gothenburg, Sweden-headquartered) is the world's largest ferry ship owner and operator. The company provides freight and travel services on routes connecting the UK, Ireland, Denmark, Germany, Latvia, the Netherlands, Norway, Sweden, and Poland.

Stena's first operations were on the Goteborg-Frederikshavn (Sweden-Denmark) route. In 1972, Stena introduced a computer-based booking system for its cruise ferries. In 1978, this innovative system was implemented for freight ferries as well. The company owns three ferry ports: Holyhead and Fishguard (in Wales) and Cairnryan (Scotland). As of January 2020, Stena employs 2,500 people in the UK and Ireland. On its Irish Sea routes (between Ireland and the UK), Stena schedules 326 weekly crossings and transports 2.6 million passengers (plus 1.28 million wheeled cargo units).
In 1981, Stena acquired Sessan Line, including its two newbuilds (Kronprinsessan Victoria, Prinsessan Birgitta), which were the largest ships in Stena's fleet at the time. In 1983, Stena acquired Varberg-Grena Linjen (operated separately under the Lion Ferry brand until 1997). In 1989, Stena acquired SMZ (Stoomvaart Maatschappij Zeeland), which operated as Crown Line. In 1990, Stena acquired Sealink British Ferries (owned by Sea Containers), which was rebranded as Stena Line UK and currently operates all Stena ferries on its routes between Ireland and the UK. In 2000, Stena acquired Scandlines.
In 1996, Stena launched three new high-speed vessels (with a passenger capacity of 1,500) on the routes Belfast-Stranraer, Holyhead-Dun Laoghaire, and Hoek van Holland-Harwich. A smaller high-speed ship (with a passenger capacity of 900) was launched on the Goteborg-Frederikshavn route.
In 1998, Stena merged its Dover-Newhaven operations with "P&O European Ferries" to form the joint venture "P&O Stena Line" (40% Stena, 60% P&O). In 2002, P&O bought out Stena's shares and became the sole owner, renaming the company "P&O Ferries."
In November 2006, Stena placed an order for two superferries (the largest ships in the company's fleet, each with a gross tonnage of 62,000 tons). In 2010, the shipbuilder Aker Yards (now STX Europe) delivered the sisterships Stena Hollandica (May 16) and Stena Britannica (October 9). These new ferries were deployed on the North Sea route Hoek van Holland-Harwich.
In 2010, Stena acquired DFDS's Northern Ireland operations on the Belfast-Heysham-Birkenhead route. In 2012, Stena launched Superfast 7 and Superfast 8 on the Belfast-Stranraer route. In 2014, Stena acquired Celtic Link's service from Rosslare Europort to Cherbourg. On its Irish Sea routes, Stena ferries approximately 3 million passengers annually, more than its rivals combined.
From 2012 to 2017, Stena's Belfast ferry services (to Cairnryan, Birkenhead-Liverpool, and Heysham) grew by 15% (car volumes), 13% (passenger traffic), and 19% (freight traffic). Stena Line operates from Belfast with seven ships and 22 daily crossings.
In 2017, the company ordered six vessels (sisterships of the E-Flexer series) from AVIC Weihai Shipyard (China). Each has a capacity of 1,000 passengers, 120 cars, and 3,100 lane meters (210 trailers). Deliveries were planned for 2020-2022.
In June 2018, Stena partnered with Hitachi to implement fleet-wide artificial intelligence technology to reduce fuel consumption costs. In 2019, Stena RoRo purchased Yamato (2003-built, IMO 9263150) from Hankyu Ferry (Japan). The vessel was drydock-rebuilt in Europe and then chartered out in 2020.
In 2020, STENA permanently closed the Sweden-Germany route Trelleborg-Sassnitz (Rugen Island) and upgraded the Sweden-Germany freight route Liepaja-(Karlskrona)-Travemunde. Celebrating the 25th anniversary of the Holyhead-Dublin/UK-Ireland service (launched on November 18, 1995, with Stena Traveller), Stena served over 12 million passengers, approximately 3 million cars, and around 3.5 million freight units. As of 2021, Stena offers 238 weekly UK-Ireland crossings.
In 2020-2021, Stena RoRo enlarged and upgraded two ships (Lagan-Scandica, Mersey-Baltica) by 30% and renamed them. Both ferries were deployed on the Sweden-Latvia route Nynashamn-Ventspils. In February 2020, the Sweden-Denmark freight service Halmstad-Grenaa was inaugurated.
In 2021-2025, two fully electric ships were designed and ordered for the Sweden-Denmark route Gothenburg-Frederikshavn.
STENA is the Irish Sea's largest ferry company with the biggest fleet and most Ireland-UK routes (228 weekly crossings). STENA also serves the routes Dublin-Holyhead (Wales) and Rosslare-Fishguard (Wales) and has a direct service Rosslare-Cherbourg (France). The bi-daily service Hanko-Nynashamn (Finland-Sweden) was inaugurated in January 2022 and discontinued in October 2023. The Rosslare-Cherbourg service was discontinued in 2024 (passenger) and terminated in 2025 (cargo).
In July 2021, STENA RORO ordered two additional EFlexer ships (bringing the total to 12) from CMI Jinling (Weihai, China), with deliveries scheduled for 2024-2025. Most EFlexers are long-term chartered to BRITTANY FERRIES (UK-France routes). The new ships' passenger capacity is 1,400, and cargo capacity is 2,377 lanemeters (EFlexer 2024/route Portsmouth-Caen) and 2,517 lanemeters (EFlexer 2025/route Portsmouth-St Malo).
In 2025, STENA acquired Wasaline from NLC Ferry, starting the Finland-Sweden service (Vaasa-Umea) with Aurora Botnia (shipowner Kvarken Link).
TT LINE
TT LINE (routes, fleet, ttline.com, 1962-founded, headquartered in Lubeck, Germany) is a German shipping company operating Baltic Sea routes between Sweden and Germany (Trelleborg-Travemunde and Trelleborg-Rostock) and between Sweden and Poland (Trelleborg-Swinoujście).

The company's name, "TT-Line GmbH," is an abbreviation of "Travemunde-Trelleborg Line." TT LINE's Sweden-Germany service (Trelleborg-Travemunde) has been operational since 1962. In 1978, the company acquired 50% of Olau Line (Denmark), and the remaining shares were purchased in 1979. Olau Line operated between 1956-1994 and, from 1974 to 1994, connected the UK and the Netherlands (Sheerness-Vlissingen).
In 1980, TT LINE and Saga Linjen (a Swedish State Railways subsidiary) established the "TT Saga Line" brand. With six ships, it connected Travemunde with Trelleborg, Malmo, and Helsingborg. Malmo-Helsingborg services were discontinued in 1982, and Saga Linjen closed in 1991.
In 1992, the Trelleborg-Rostock service started with 50% ownership by DSR (Deutsche Seereederei). The rebranded company ("TR-Line") was fully acquired in 1996 and renamed "TT-Line."
In 2006, TT-Line moved its headquarters from Hamburg to Lubeck.
In January 2014, TT-Line began the Sweden-Poland service Trelleborg-Swinoujście.
In June 2017, TT-Line started the Denmark-Poland service Ronne-Swinoujście.
DFDS SEAWAYS
DFDS Seaways (routes, fleet, dfdsseaways.co.uk, 1866-founded, headquartered in Copenhagen, Denmark) operates shipping routes in Northern Europe (Baltic Sea and North Sea).

In July 2010, DFDS acquired Norfolkline (a Maersk-owned ferry shipping and logistics company) and merged its divisions ("DFDS Tor Line" and "DFDS Lisco") into "DFDS Seaways."
Norfolkline (1961-founded) provided cargo ferry services in Northern Europe (English Channel, Irish Sea, North Sea), as well as passenger ferry services (English Channel, Irish Sea) and logistics. Upon acquisition, Norfolkline had over 2,200 employees and offices in 13 European countries. Its fleet included 18 vessels, plus hundreds of trailers (including refrigerated, dry-cargo, and swap-body). In 2006, the company handled over 1.5 million ferry passengers on routes like Dover-Dunkirk, Liverpool-Belfast, and Liverpool-Dublin.
In February 2012, the Dover-Calais route was launched. In 2015, DFDS updated its logo, which was first introduced on the Cote des Dunes and Cote des Flandres. The other fleetmates soon dropped the "Seaways" suffix from their names.
2017 was a record year for DFDS, with an operating profit of DKK 2.7 billion. The increased volumes were partly due to DFDS' 10 North Sea freight routes, which saw a 7% growth over 2016. In 2017, the company ordered four RoPax newbuilds (with a capacity of 475 trailers each) specifically for North Sea crossings. The ferries were ordered from the Jinling Shipyard (China) with deliveries scheduled from 2019 onward.
In 2018, DFDS invested around DKK 100 million (USD 16.5 million) to further develop the company's digital capabilities, new online booking systems (for passenger-shipping-logistics), and new mobile apps (serving passengers, drivers, and freight customers).
On April 12, 2018, DFDS acquired 98.8% of Turkey's largest freight shipping company, "UN Ro-Ro Anasayfa," for EUR 950 million. UN Ro-Ro operates 5 Mediterranean routes connecting Turkey with Greece (Patras), Italy (Trieste, Bari), and France (Toulon). It has 12 vessels, 3 port terminals (Trieste, Ambarli, Pendik-Istanbul), and annual revenue of EUR 240 million, employing around 500 people.
In 2018, DFDS and STENA signed a 10-year bareboat charter deal for the Cote d'Opale (modified E-Flexer), which began Dover-Calais crossings in June 2021.
In May 2019, DFDS and Stora Enso Oyj (a Finnish manufacturer of paper, pulp, forest products, and biomaterials, 1998-founded) signed a 5-year agreement (+3 years optional) to ship approximately 700,000 tons of cargo via DFDS ships on the new Sweden-Belgium route Goteborg-Zeebrugge/Ghent. Stora Enso's annual sales are approximately EUR 10.5 billion. The Goteborg-Zeebrugge line opened in June 2019 with 3 ships and 5 weekly departures in each direction.
On January 2, 2021, a direct Ireland-France service (Rosslare-Dunkirk) was launched with 6 weekly crossings.
In December 2022, DFDS acquired McBurney Transport Group (1965-founded, based in Ballymena, Northern Ireland), specializing in trailer-based logistics by road and ferry between Ireland and the UK.
In September 2023, DFDS acquired FRS Iberia/Maroc (a division of FRS GmbH & Co KG, 2000-founded). FRS Iberia groups three independent companies operating under the Maroc brand. It manages three short routes connecting Spain and Morocco via the Gibraltar Strait (Tarifa-Tangier, Algeciras-Ceuta, Algeciras-Tanger Med) with 7 vessels. The passenger ferries are high-speed and feature catamaran-designed hulls. As of 2023, Maroc holds approximately 30% market share in Gibraltar Strait ferry crossings.
In May 2024, it was announced that the Oslo-Copenhagen route would be sold to Gotlandsbolaget/Rederi Gotland AB.
BRITTANY FERRIES
Brittany Ferries (routes, fleet, brittanyferries.com, 1972-founded, headquartered in Roscoff, France) is a French company serving shipping routes between France-UK and France-Spain. Brittany Ferries is one of the largest ferry and cruise tour operators from the UK and Ireland to France and Spain. Bookings can be made through travel agents or directly online (except for golf breaks).

Brittany Ferries began operations in January 1973 with the Plymouth-Roscoff service and soon expanded with routes to Saint-Malo, Santander, and Cork. In 1985, it acquired Truckline Ferries (a freight-only operator with 2 ships serving Poole-Cherbourg). In 1986, the Caen-Portsmouth and Caen-Poole routes were introduced. In 1989, the Cork-Santander service began.
In 2001, a fast-ferry service between Poole and Cherbourg was launched through a partnership with Condor Ferries. Freight-only services began in 2007 (Poole-Cherbourg), 2009 (Poole-Santander), and 2016 (Poole-Bilbao). In 2011, the Portsmouth-Bilbao line was inaugurated. On May 13, 2011, the new Portsmouth Continental Ferry Port was officially opened, serving cruise companies, Condor Ferries (to the Channel Islands), and Brittany Ferries. In May 2013, the Portsmouth-Le Havre/Paris route was introduced.
In 2018, Brittany Ferries confirmed two STENA LINE-charter deals for two Stena E-Flexer class ships (Galicia, Salamanca), with a buy-option after their 5-year charters. In April 2018, the Cork-Santander line was started (terminated in 2020). In October, a new logo was introduced, which was implemented fleetwide during drydocks in 2018-2019-2020.
As of 2018, Brittany Ferries operates 12 liners on 11 routes, with an annual capacity of approximately 2.5 million passengers (85% British) and 210,000 wheeled freight units. In 2018, the company invested GBP 450 million in fleetwide renovations and three LNG-powered E-Flexers.
In March 2020, Brittany Ferries and Columbia Threadneedle ESIF (European Sustainable Infrastructure Fund) finalized the acquisition of Condor Ferries. The company was purchased from MIRA (Macquarie Infrastructure and Real Assets), part of MGL-Macquarie Group Ltd (an Australian investment bank and financial company).
Since March 2021, Brittany Ferries has operated the Ireland-France route Rosslare-Cherbourg as part of the 2020-launched service Rosslare-Bilbao (Ireland-Spain). Also since March 2021, the company has chartered MS Cotentin for the route Portsmouth-Le Havre.
The company offers the following 4 main products (all include ferry travel):
- Land Accommodations (cottages and villas in France and northern Spain)
- Hotel Breaks (to France, Spain, and Portugal, including hotel chains Paradores and Pousadas, car tours, B&B hotels, and apartment rentals in Portugal and southern Spain)
- Family Holidays (apartments, chalets on 5 campsites in northern Portugal, holiday resorts in France and northern Spain)
- Golf Breaks (courses in France and northern Spain)
On October 24, 2016, the company announced plans to build a new LNG-powered cruise ferry for the UK-France route Portsmouth-Caen. On December 21, 2016, the vessel's design (project "Mont St Michel 2") was revealed—capacity 1680 passengers and 550 cars (or 130 freight vehicles) with a gross tonnage of 42,000 tons. The shipbuilder is Flensburger Schiffbau-Gesellschaft (shipyard Flensburg, Germany) with a scheduled delivery date of April 30, 2019.
In May 2018, the company launched the first-ever direct link from Ireland to Spain (Cork-Santander), with 2 weekly return crossings, plus 1 weekly return crossing from Cork to Roscoff. In 2018, the company also celebrated its 40th year of operations in Ireland (since 1978, on the Cork-Roscoff route).
The company's 2019 schedule was expanded with 19 more weekly return crossings across the English Channel, from Roscoff to Plymouth, Cherbourg to Poole, and Le Havre to Portsmouth. As requested by the UK's Department for Transport, the additional crossings increased the company's freight capacity by approximately 50%, and overall cross-channel capacity by 30%.
In mid-November 2019, Brittany Ferries and ESIF (Columbia Threadneedle European Sustainable Infrastructure Fund, an equity fund part of Columbia Threadneedle Investments UK) signed an agreement to acquire Condor Ferries from MIRA (Macquarie Infrastructure and Real Assets Ltd). The company was owned by MIRA via its subsidiary Commodore Group (part of Macquarie Group).
Annually, the company serves approximately 2.5 million passengers and 210,000 freight vehicles.
BC FERRIES
BC FERRIES (routes, bcferries.com, 1960-founded, Victoria, BC Canada-headquartered) is a Canadian state-owned company. "British Columbia Ferry Services Inc." provides daily scheduled passenger and vehicle (RoPax) ferry services between mainland Canada and British Columbia (BC) islands. BC's inland ferries (on lakes and rivers) are operated by the state's Ministry of Transportation.

Currently, the company is ranked as North America's largest ferry operator (followed by "Washington State Ferries") and the world's third-largest passenger ferry line.
In 2008, the company launched three Coastal-class vessels (the sister ships Coastal Renaissance, Coastal Inspiration, Coastal Celebration) ranked as the world's largest double-ended passenger ferries (maximum capacity 1650 passengers, 370 cars). The fleet's largest by passenger capacity (2100 passengers, 358 cars) are the two Spirit-class ships (Spirit of British Columbia, Spirit of Vancouver Island).
In April 2018, the senior citizens' discount was reinstated—passengers aged 65 and older can travel for free (Monday through Thursday) on most routes.
On October 5, 2018, the company issued an REOI (Request for Expressions of Interest) for the construction of 5 new ships. The competitive bidding was open to shipyards worldwide. The new builds are scheduled to enter service in 2023 on the Metro Vancouver-Vancouver Island routes.
In March 2019, BC Ferries announced plans to build up to 5 new ships, replacing 4 existing vessels (New Westminster, Alberni, Coquitlam, and Cowichan), and adding capacity to the Metro Vancouver-Vancouver Island route. The new builds were scheduled to enter service in mid-2020.
BC FERRIES' current fleet consists of 36 vessels (total capacity 27,000+ passengers and crew) and serves 47 locations along BC's coastline. The fleet's car capacity ranges from 16 to 470 (super ferries). From 2008 to 2018, BC Ferries invested over CAD 1 billion in BC Canada shipyards, including Vancouver Drydock (Seaspan), Point Hope Maritime (Victoria, BC), Esquimalt Drydock (Esquimalt, BC), Esquimalt Graving Dock (Victoria, BC), Allied Shipbuilders (North Vancouver), and Deas Dock (Fleet Maintenance Unit, Richmond, BC). BC Ferries contracts local suppliers for fleet-wide upgrades, including repairs, drydocking, and refits. BC Ferries spends approximately $200 million annually on ships, port terminals, and technologies, generating about $100 million in government taxes and supporting over 5,100 local jobs.
PO FERRIES
P&O Ferries (routes, fleet, poferries.com, 2002-founded, Dover, England-headquartered) operates shipping routes between the UK and France, the UK and Ireland, the UK and Holland (mini-cruises), the UK and Belgium (mini-cruises), and Scotland and Northern Ireland.

In 2006, the P&O Group was sold to DP World, a Dubai-based company that owns and operates inland and seaport terminals worldwide and specializes in maritime services and logistics. DP World acquired P&O Group but sold P&O Ferries to Dubai World Holding (its majority shareholder), as DP World focused on container terminal operations. In February 2019, DP World reacquired P&O Ferries for GBP 322 million (UAE dirham 1.5 billion).
In September 2010, the ferry route Portsmouth-Bilbao was discontinued, marking the end of the Pride of Bilbao (now Princess Anastasia) ship charter. This was the last P&O service from Portsmouth, following the closures of the Portsmouth-Cherbourg and Portsmouth-Caen routes in 2004, and the Portsmouth-Le Havre Paris route in 2005.
The cheapest P&O mini-cruise ferry deals are 3-day / 2-night voyages from the UK to Holland and Belgium. Themed as "city breaks," P&O mini-cruise deals offer roundtrip departures from Hull to either Rotterdam (Amsterdam) or Zeebrugge (Brugge). Longer city breaks (up to 7 days / 6 nights) offer roundtrips to Hamburg (Germany), Bilbao (Spain), and La Rochelle (France). On mini-cruises from the UK, P&O ferry passengers receive boarding cards (which also function as meal vouchers), cabin keycards, and booklets with vouchers (for return check-in and bus transfers, if applicable). A boarding card with a suitcase icon indicates passengers can leave their luggage in the stateroom while disembarking, but this feature must be confirmed at check-in.
In June 2018, P&O increased its freight shipping capacity by 25% (to about 125,000 units annually) on the Belgium-UK route Zeebrugge-Teesport. Teesport (owned by PD Ports) opened a new rail connection to Mossend (near Glasgow, England).
In February 2019, DP World PLC (Dubai) acquired P&O Ferries (pan-European logistics) and P&O Ferrymasters (supply chain solutions in Europe) for GBP 322 million (USD 421 million). P&O Ferries' FY2017 reports included revenue of GBP 1.1 billion (USD 1.4 billion) and EBITDA of GBP 100 million (USD 131 million).
In 2019-2020, the company will build the Tilbury2 ferry terminal—a dedicated deepwater berth at Thames River. The new terminal, with a building cost of GBP 150 million, has an annual freight capacity of 600,000 units. The facility is situated on a 152-acre site (part of the former "Tilbury Power Station") and is directly linked to the A13 via a new road.
In April 2021, P&O sold the ships Pride of Brugge and Pride of York (GNV Aries) to GNV, after terminating the Hull-Zeebrugge service in January.
In December 2023, P&O discontinued the Dublin-Liverpool service after Liverpool's berth lease was not extended by the port owner. This decision impacted 24 weekly UK-Ireland crossings.
TALLINK-SILJA LINE
Tallink-Silja (routes, fleet, tallinksilja.com, 1989-founded, Tallinn, Estonia-headquartered) is ranked as the Baltic Sea's largest ferry operator by fleet tonnage and capacity. The company operates under two brands: Tallink (parent company) and the subsidiary Silja Line.
Tallink-Silja ships provide direct connections from Estonia to Finland and Sweden, with additional routes connecting Sweden to Finland and Latvia.

Currently, Tallink-Silja offers 1-2 overnight cruises, hotel and travel packages, city breaks, daily passenger and cargo shipping, and high-speed ferry shuttle services.
The company's history dates back to Soviet Union times, when the Estonian Shipping Company was established in 1965 to provide passenger ferry service on the Helsinki-Tallinn route. Year-round operations began in 1968.
In 2006, AS Tallink Grupp purchased Baltic services from Superfast Ferries for EUR 310 million and opened the Riga-Stockholm route. In the same year, Tallink acquired Silja Line from Sea Containers Ltd for EUR 470 million.
In August 2011, STENA chartered two ships (Superfast 7, Superfast 8) through 2014 for the Scotland-Northern Ireland routes.
In 2014, Tallink's asset base was EUR 1.7 billion, of which EUR 1.02 billion was invested in new builds, and EUR 780 million was spent on acquisitions. The company's loans amounted to EUR 440 million. Annual spending on ship refurbishments and fleet upgrades is around EUR 30 million.
In February 2015, Tallink signed a shipbuilding contract with Meyer Turku for the Megastar (2017) and in March 2018 with RMC-Rauma for the MySTAR (2022). Both new builds are the fleet's largest (GT 50,000), LNG-powered, and have a passenger capacity of 2800 each.
In 2016, Tallink operated a fleet of 16 vessels and 5 hotels. Tallink's annual revenue was EUR 938 million, with 7,000 employees and an annual passenger capacity of 9.5 million. The annual cargo capacity was 328,000 units. Over half of the total revenue came from restaurant and duty-free shop sales, and a quarter from ticket sales.
In FY2017, Tallink Grupp ferried 9.76 million passengers (+3.2% over 2016) and 364,296 wheeled cargo units (+11%). The Estonia-Sweden route served 1.01 million passengers. Latvia-Sweden traffic increased by 45.8%, and Estonia-Finland traffic increased by 11.6%.
In FY2019, Tallink Grupp served a record 9.76 million passengers (+0.1% over 2018's 9.76 million). The number included 2.89 million (Finland-Sweden routes), 5.12 million (Finland-Estonia), 0.80 million (Latvia-Sweden), and 0.95 million (Estonia-Sweden).
Since September 2020, Tallink-Silja has operated the Tallinn-Mariehamn-Aland-Stockholm route with two ferries (Baltic Queen and Victoria I) and two return trips weekly. Departures are from Tallinn (D-terminal) and Stockholm (Vartahamnen).
FINNLINES
Finnlines (routes, fleet, finnlines.com, 1947-founded, Helsinki, Finland-headquartered, part of the Grimaldi Group) provides passenger and ro-ro ferry services predominantly in Northern Europe (Baltic Sea and North Sea).
Finnlines' ships connect the countries Finland, Russia, Sweden, Germany, Poland, Denmark, Holland, Belgium, the UK, and Spain.

The company was founded as a subsidiary of Merivienti Oy ("Sea Export Ltd") for transatlantic freight services (mainly forest industry products) between Finland and the USA. Passenger ferry services began in 1962 on the Finland-Sweden-Germany route Hanko-Visby-Travemunde.
In 1973, Finnlines ordered the GTS Finnjet from the Wärtsilä Helsinki shipyard. At the time, it was the world's largest and fastest ship (GT 24,605 tons, length 213 m, speed 31 knots / 57 kph / 36 mph). The vessel entered service in May 1977 on the Helsinki-Travemunde route (crossing time was 22 hours).
In 2004, the brands Finnlink and NordoLink merged into Finnlines. Also in 2004, shipbuilding orders were placed for five large Star-class ferries (from Fincantieri, Italy - shipyards in Ancona and Castellammare di Stabia) delivered in 2006 and 2007. In August 2007, Finnlines ordered six new ice-class ships (from CSC Jinling Shipyard, Jiangsu, China), with planned deliveries in 2010 and 2011.
From 1999 to 2001, the four Seapacer-class ships (built by Astilleros Españoles in the Cadiz / Puerto Real shipyard) were delivered: Finnclipper, Finneagle, Stena Britannica (Finnfellow), and Stena Germanica - all with ice-strengthened hulls.
In January 2007, Finnlines' largest shareholder, Grimaldi Group, expressed its intention to purchase the entire company. Grimaldi completed the acquisition of Finnlines (100% ownership) in August 2016.
From October 2017 to May 2018, Finnlines completed a ship lengthening project for all six ice-class "1A" RoRo vessels of the "Finnbreeze series" (Finnsky, Finnsun, Finntide, Finnwave, Finnbreeze, and Finnsea). Each of these Nanjing, China-built vessels was enlarged by adding an approximately 30 m long midship section. Following the EUR 90 million budgeted vessel reconstruction program, each ship's capacity increased by 30% (from 3,291 to 4,213 lane meters). The drydock refits were done at the Remontowa shipyard in Gdansk, Poland.
For the fiscal year 2017, Finnlines Group reported a record year with a 21% increase (over 2016), reaching EUR 82.7 million in revenue. Finland's sea freight volumes in 2017 grew by 12%. From 2007 to 2017, the company spent over EUR 1 billion on fleet renovation and port infrastructure projects.
In May 2018, Finnlines and CSC Jinling Shipyard (China) signed a shipbuilding contract for five ships (three Ro-Ro plus two Ro-Pax), with scheduled deliveries from 2021 to 2023 and a total cost of approximately EUR 500 million.
In May 2018, Finnlines started a direct/weekly cargo service from Helsinki to Aarhus (Denmark), connecting with Turku via Travemunde. Departures from Helsinki are on Thursdays, and Sundays departures from Helsinki to Aarhus are via Travemunde (arrival on Tuesday morning).
COLOR LINE
Color Line (routes, fleet, colorline.com, 1990-founded, Oslo, Norway-headquartered) operates passenger and cargo shipping routes between Norway and Sweden, Germany, and Denmark.

Color Line is Norway's largest cruise ferry operator (in terms of fleet capacity) and also one of Europe's leading companies in terms of fleet age (all newbuilds from the year 2000 onward) and shipboard amenities (staterooms, shops, bars, restaurants, and lounge entertainment).
The company has offices in Norway (Oslo / main, Kristiansand, Sandefjord, Larvik), Germany (Kiel), Denmark (Hirtshals), and Sweden (Stromstad).
The company was established following the 1990 merger of the Norwegian ferry companies Jahre Line and Norway Line. Jahre Line operated the Oslo-Kiel route since 1961. Norway Line operated routes connecting Norway with the UK and Holland since 1986. Also in 1990, the newly formed Color Line acquired Fred Olsen Lines, along with its operations between Norway and Denmark.
In the 1990s, the company expanded its fleet by purchasing larger second-hand ferries. In October 1996, Color Line acquired Larvik Line and its Norway-Denmark services. In September 1998, the company acquired Color Hotel Skagen and Scandi Line (operating short Norway-Sweden routes). At the end of 1998, Color Line sold its Norway-UK operations to FJORD LINE. In 1999, the company acquired Scandi Line (renamed Color Scandi Line).
The 2000s were the company's fleet renovation period, with the launch of Color Fantasy (2004), Color Magic (2007), Superspeed 1 (2008), and Superspeed 2 (2008). In May 2008, the Oslo-Hirtshals route was officially closed.
In January 2017, Color Line signed a letter of intent with the Ulstein Verft shipyard (Ulsteinvik, Norway) for building a new ship (Color Hybrid) for the Sandefjord-Stromstad route. To support the ship, Color Line installed shore-to-ship power facilities in Oslo, Kristiansand, Larvik, and Sandefjord in 2017, where the ship's batteries can be charged.
Since January 1, 2019, the Norway-Germany route (Oslo-Kiel) has been served with three weekly round trips by the Finncarrier (freight RoRo ship, capacity 1,775 lane meters / 120 trucks) and the cruise ferries Color Magic and Color Fantasy.
Currently, Color Line is the only cargo-passenger shipping company with Norwegian-flagged vessels serving international traffic with regularly scheduled crossings to/from Norway.
MOBY LINES
Moby Lines (routes, fleet, mobylines.com, 1959-founded, Milan, Italy-headquartered) operates shipping routes connecting mainland Italy and France with the Mediterranean islands Corsica, Elba, and Sardinia.
The company is best known for using Warner Bros' patented Looney Tunes characters for its ships' interior decorations.

Since 1996, Moby's fleet has been radically expanded with newly built, larger, and faster vessels.
In 2003, the parent company (shipowner) Onorato Armatori SpA signed an exclusive agreement with Warner Bros (a division of Time Warner Corporation) to paint the largest Moby ships' hulls with Looney Tunes-themed liveries.
In February 2018, MSC Group and Moby Lines signed a shipbuilding contract with the Chinese companies GSI (Guangzhou Shipyard International) and CSTC (China Shipbuilding Trading Co) for four ships. Each ship has a passenger capacity of 2,500, a cargo capacity of 3,800 lane meters (1,300 cars or 3,000 trailers), length of 237 m, and speed of 24 knots. The contract includes the option for an additional four ships of the same design. Two of the new builds (1st and 3rd) are for GNV, the other two (2nd and 4th) are for Moby Lines.
GRIMALDI LINES
Grimaldi Lines (routes, fleet, grimaldi-lines.com, 1999-founded, Civitavecchia, Italy-headquartered) operates mainly on Mediterranean shipping routes connecting mainland Italy with Sardinia, Sicily, Spain, Greece, Morocco, and Tunisia.
The company is a subsidiary of Grimaldi Group (1947-founded).

The company was founded for shipping services within the "Autostrade del Mare" ("Motorways of the Sea" - a development project aimed at improving the European Union's maritime transportation links).
The company started the first freight ferry connections between Italy, Spain, and Malta, and since 2000 has carried passengers on routes connecting Italy (ports Civitavecchia and Salerno) with Sicily (Palermo), Spain (Barcelona), France (Toulon), Corsica Island (Porto Vecchio), and Tunisia (Tunis). Over the years, lines to Sardinia Island, Greece, and Morocco were added.
In 2021, Grimaldi won the tender for the route Naples-Cagliari Sardinia-Palermo Sicily. Operated with MS Corfu (960-pax), the twice-weekly service offers departures from Naples (Mondays and Fridays at 7 PM), Cagliari (Thursdays at 7 PM), and Palermo (Wednesdays at 7 PM).
GNV (Grandi Navi Veloci)
Grandi Navi Veloci (routes, fleet, gnv.it, 1992-founded, Genoa, Italy-headquartered) owns ferries connecting mainland Italy with Sicily, France, Sardinia, Albania, Morocco, and Tunisia.
The company was founded by Aldo Grimaldi as a Grimaldi Group subsidiary, with operations starting in 1993 (Genoa-Palermo Sicily route).

The sister ships Majestic (1993) and Splendid (1994) were the first-ever Italian cruiseferries.
In the following years, more vessels were introduced, serving the routes Livorno-Palermo, Civitavecchia (Rome)-Palermo, Genoa-Olbia (Sardinia Island), Genoa-Barcelona (Spain).
GNV's ships La Superba (2002) and La Suprema (2003) were the Mediterranean's largest at that time.
The fleet expansion in 2008 added three Ro-Ro cargo vessels (Audacia, Tenacia, and Coraggio), serving the newly opened Genoa-Barcelona-Tangier route.
In 2009, GNV became fully independent from Grimaldi Group, and in 2010 was acquired by MSC Group. In 2010, GNV merged with SNAV (Societa Navigazione Alta Velocita/also an MSC subsidiary). In 2012, new routes to Italy-France (Sete) and Italy-Morocco (Tangier, Nador) were opened.
In December 2014, Grimaldi Holding sold the ship Audacia to the Hong Kong-based Rizhao Port Shipping Company Ltd. The boat (renamed "Rizhao Orient") serves the China-South Korea route Rizhao-Pyeongtaek. In 2015, the Italy-Albania (Durres-Tirana) route was opened.
In February 2018, MSC Group and Moby Lines signed a shipbuilding contract with the Chinese companies GSI (Guangzhou Shipyard International) and CSTC (China Shipbuilding Trading Co) for four new luxury cruise ferries. Each ship has a passenger capacity of 2,500 (536 cabins), a cargo capacity of 3,765 lane meters (750 cars or 250 trailers), a length of 230 m (755 ft), and a speed of 24 KN. The contract includes the option for an additional four ships of the same design. Two of the new ships (1st and 3rd) are for GNV, the other two (2nd and 4th) are for Moby Lines. The first ship's delivery was scheduled for 2020. Both Chinese shipbuilders are subsidiaries of the state-owned corporation CSSC (China State Shipbuilding Corporation).
In April 2021, P&O Ferries sold the ships Pride of Bruges (Antares) and Pride of York (Aries) to GNV, after terminating the Hull-Zeebrugge service in January. Also in 2021, GNV bought the ship Sealand (formerly Scottish Viking) and chartered GNV Bridge.
In January 2022, MSC ordered four cruiseferries (1,500 pax / 303 cabins) for GNV from the shipbuilder CSI-Guangzhou Shipyard International (China). Deliveries are scheduled for 2024-2027.
TIRRENIA di Navigazione
Tirrenia Navigazione (routes, fleet, tirrenia.it, 1936-founded, headquartered in Naples, Italy and Cagliari, Sardinia) is a privately owned company contracted by Italy's Ministry of Transportation to provide regularly scheduled shipping services between mainland Italy and the country's main islands.
The company serves exclusively domestic routes.

The company was founded following the 1936 nationalization of privately owned Italian shipping lines. After World War II (1939-1945), its few surviving vessels were used to connect the largest Italian islands (mainly Sardinia) with mainland Italy.
On December 23, 2009, the company was put on the market. Among the 16 bidding companies were SNAV, GNV, Grimaldi Lines, Moby Lines, Corsica-Sardinia Ferries, and Mediterranea Holding. The latter ended up as the sole bidder when all other companies withdrew. On July 28, 2010, Mediterranea Holding won the bidding for Tirrenia and its subdivision, Siremar (Sicilia Regionale Marittima). However, on August 4, it was announced that the sale was off as Mediterranea Holding failed to show up for the signing.
Until 2010, Siremar operated routes between Sicily and the Italian islands of the Aeolian, Aegadian, Ustica, Lampedusa, and Pantelleria.
In November 2008, the Italian government began procedures for Tirrenia's privatization. On May 18, 2011, the second purchase tender was won by CIN (Compagnia Italiana di Navigazione), a new company formed specifically for Tirrenia's privatization, consisting of Grimaldi Group, Moby Lines (Vincenzo Onorato), and Marinvest (Gianluigi Aponte). In April 2012, CIN and private investors (including Alexis Tomasos) won the tender, and on June 21, the state-owned company was officially privatized. The EU Antitrust Authority's decision to accept CIN's dominant position led to the exit of Grimaldi Group, Moby Lines, and Alexis Tomasos. On July 19, CIN officially became the company's owner.
Annually, Tirrenia Navigazione operates numerous crossings (around 60,000) using new high-speed ferries. The annual number of passengers served is around 13 million, with about 2 million cars transported. The fleet's annual mileage is also impressive—around 6.5 million km (4 million miles). On the most popular routes, ships have a capacity of approximately 2,700 passengers (900 cars). During the summer high season, these vessels cruise at speeds of up to 55 kph (35 mph).
IRISH FERRIES
Irish Ferries (routes, fleet, irishferries.com, 1992-founded, Dublin, Ireland-headquartered) is a division of ICG (Irish Continental Group) operating passenger and freight services between Ireland, the UK, and Europe.

ICG (1972-founded as Irish Continental Line) also operates terminal facilities in Dublin (Ferryport Terminals) and Belfast (Container Terminal). Until 1992, when ICG acquired the state-owned B&I Line (British and Irish Steam Packet Company), ICG operated only on routes between Ireland and Europe. Following the acquisition of B&I Line, services were expanded to include short routes between Ireland and the UK. ICG's container shipping and port operations were also extended. The company's fleet was fully modernized by replacing all existing vessels with newbuilds (a EUR 500 million investment project).
In 2016, ICG signed an agreement with the shipbuilder FSG (Flensburger Schiffbau-Gesselschaft) for a future cruise ferry building order. At a contract price of EUR 144 million, the new ship (scheduled for delivery in May 2018) is designed with a pax-crew capacity of 1,885, 435 cabins (four cabin decks, including balcony suites), 165 freight vehicles (2,800 lane meters), and an additional car deck (total capacity 300 cars). The new ship will feature bars, restaurants (à la carte and self-service), a Club Class passengers-only lounge (with direct access from the car decks), two cinemas, freight drivers-only facilities, retail shops, and pet facilities. The ship will be powered by four diesel engines (total power output 33.6 MW).
After the delivery of the WB Yeats ship, the shipbuilder Flensburg began construction of a second, larger cruise ferry, scheduled for delivery in 2020. The newbuild was commissioned in mid-January 2018 by the parent company Irish Continental Group at a contract price of EUR 165.2 million.
Since April 2021, the Ireland-Wales route Rosslare-Pembroke Dock has been operated by the chartered Blue Star 1 from Attica Group.
Since June 2021, the new England-France route Dover-Calais has been operated with the Isle of Inishmore, which is currently chartered to Interislander (KiwiRail, New Zealand) under the name "Kaitaki." In January 2018, the HSC Jonathan Swift (fast catamaran ferry, aka Dublin Swift) was sold to Balearia for EUR 38.8 million. The catamaran operated on the Dublin-Holyhead route from 1999 to 2017 and was replaced by the Westpac Express (a 2001-built high-speed catamaran).
BALEARIA
Balearia Eurolineas Maritimas (routes, fleet, balearia.com, 1998-founded, Denia, Spain-headquartered) operates Mediterranean shipping routes connecting mainland Spain with the Balearic Islands. Departures are from Barcelona, Denia, and Valencia.
The company also operates routes passing through the Strait of Gibraltar, with departures from Algeciras to Ceuta (Spanish Morocco) and Tangier (Morocco).

In 2011, the company introduced the "Balearia Caribbean" brand, which operated regular cruise ferry services between the USA and the Bahamas (round trips from Fort Lauderdale, Florida to Freeport, Grand Bahama Island). In March 2015, the high-speed catamaran Pinar del Rio (built in 1992) was replaced by the larger Bahama Mama (built in 2010). The Florida-Bahamas service was discontinued in 2017.
In 2016, the company signed a shipbuilding contract (valued at EUR 320 million) for three LNG-powered smart cruise ferries. The shipbuilder is LaNaval Shipyard (Bilbao, Spain). The first two ships will be delivered in 2018, with the third one scheduled for 2019. An additional EUR 130 million was allocated for terminal upgrades and fleet refurbishments.
In 2016, Balearia began services between Valencia and Mostaganem (Algeria) and Melilla-Malaga-Almeria. In 2017, Balearia transported over 3.7 million passengers and 5.6 million lane meters of cargo (around 330,000 trucks). The fleet of 25 vessels sailed over 1.2 million miles (around 2 million km). The company has over 1,500 employees and reported an annual turnover of EUR 362 million.
In August 2018, Balearia announced a EUR 60 million (USD 70.2 million) fleet renovation project to convert five cruise ferries (by 2020) to run on LNG. The vessels scheduled for dry-docking include Abel Matutes, Bahama Mama, Martin i Soler, Napoles, and Sicilia. As a result, over 45,000 tons of CO2 and 4,400 tons of NOx will be reduced annually, with sulfur and particulates completely eliminated. In August 2018, Balearia acquired Visemar One (for EUR 55 million / USD 62.4 million), expanding its fleet to 26 owned units (out of 30 total).
In October 2018, Balearia contracted Caterpillar Marine to install MAK dual-fuel engines on 3 vessels (Abel Matutes, Bahama Mama, Martin I Soler). Engine conversions (by Caterpillar dealer Finanzauto) were scheduled for early 2019. Each ship's diesel engines (2x MaK 9M43C) were replaced with 2x MaK 9M46DF (dual-fuel, power output 8.7 MW), using a gearbox and controllable pitch propellers. Caterpillar provided dual-fuel conversion kits and all modules (ignition, ventilation, exhaust gas, GVU ventilation, valves, and housing).
Itinerary of Ferries
Here are listed all CruiseMapper's ferry lines with their cruise ferry fleets, homeports (routes) and crossing times. Our list of ferries currently includes passenger vessels operated by the world's largest ferry companies:
- VIKING LINE, STENA LINE, TALLINK-SILJA LINE, FINNLINES, TT LINE
- DFDS SEAWAYS, P&O FERRIES, BRITTANY FERRIES, IRISH FERRIES
- COLOR LINE, BALEARIA, MOBY LINES, GRIMALDI LINES
- GNV (Grandi Navi Veloci), TIRRENIA, SNCM (Maritima Ferries)
- TRASMEDITERRANEA, CORSICA-SARDINIA FERRIES, CORSICA linea, NAVIERA ARMAS
- MINOAN LINES, HELLENIC SEAWAYS, BLUE STAR FERRIES, SUPERFAST FERRIES, SEAJETS FERRIES
- ANEK LINES, NEL Lines
- BC FERRIES
- MOL FERRIES Japan
- plus small-fleet companies (DESTINATION GOTLAND, CONDOR FERRIES, POLFERRIES, MARINE ATLANTIC, ECKERO LINE).
VIKING LINE
Currently, VIKING LINE ships operate on the following ferry routes:

- Aland-Sweden / Mariehamn-Kapellskar (crossing time 2,5 hours)
- Finland-Sweden / Helsinki-Mariehamn Aland-Stockholm (17 hours)
- Finland-Sweden / Turku-Mariehamn Aland-Stockholm, 10 hours
- Stockholm-Mariehamn (5,5 hours) and Sweden-Latvia (Stockholm-Riga / 17 hours, during summer)
- Finland-Estonia / Helsinki-Tallinn (2,5 hours)
STENA LINE
Currently, STENA LINE ships operate on the following passenger ferry routes:

- (Ireland-Wales UK, crossing time 3,5 hours) Rosslare-Fishguard (Irish Sea)
- (Ireland-Wales UK, 3 hours) Dublin-Holyhead (Irish Sea)
- (Northern Ireland-Scotland UK, 2 hours 15 min) Belfast-Cairnryan (Irish Sea)
- (Northern Ireland-England UK) Belfast-Heysham (the Irish Sea, freight only)
- (Northern Ireland-England UK, 8 hours) Belfast-Liverpool/Birkenhead (Irish Sea)
- (Holland-England UK, 6,5 hours) Hook of Holland-Harwich (North Sea)
- (Holland-England UK) Hook of Holland-North Killingholme Haven (North Sea, freight only)
- (Holland-England UK) Rotterdam-Harwich (the North Sea, freight only)
- (Holland-England UK) Rotterdam-North Killingholme Haven (the North Sea, freight only)
- (Sweden-Denmark, 3 hours) Goteborg-Frederikshavn (Baltic Sea)
- (Sweden-Denmark, 5 hours) Varberg-Grena (Baltic Sea)
- (Sweden-Germany, 9 hours) Goteborg-Kiel (Baltic Sea)
- (Norway-Denmark, 9 hours) Oslo-Frederikshavn (Baltic Sea)
- (Sweden-Poland, 10 hours) Karlskrona-Gdynia (Baltic Sea)
- (Sweden-Latvia, 8,5 hours) Nynashamn-Ventspils (Baltic Sea)
- (Sweden-Germany, 6 hours) Trelleborg-Rostock (Baltic Sea)
- (Germany-Latvia) Travemunde (Lubeck)-Liepaja (Baltic Sea)
The STENA LINE-owned WASALINE serves exclusively the Finland-Sweden route Vaasa-Umea (crossing time ~3,5 hours) with Aurora Botnia.
TT LINE

Currently, TT LINE ferries operate on the routes:
- (Sweden-Germany) Trelleborg-Rostock and Trelleborg-Travemunde (daily departures, crossing times 6-6,5 hours)
- (Sweden-Germany) Helsingborg-Travemunde (freight-only)
- (Sweden-Poland) Trelleborg-Swinoujscie (6 hours), and (Denmark-Poland) Ronne-Swinoujscie (5 hours)
DFDS SEAWAYS
Currently, DFDS SEAWAYS ships operate on the following passenger ferry routes:

- (English Channel /2 hours) UK England-France (Dover-Dunkirk)
- (English Channel /2 hours) UK England-France (Dover-Calais)
- (English Channel /24 hours) Ireland-France (Rosslare-Dunkirk)
- Short break "Mini Cruise" UK England-Holland /15,5 hours (Newcastle-IJmuiden / Amsterdam)
- UK England-France (Newhaven-Dieppe)
- Lithuania-Germany (Klaipeda-Kiel) 19,5 hours
- Lithuania-Sweden (Klaipeda-Karlshamn) 13 hours
- Estonia-Sweden (Paldiski-Kapellskar)
- Estonia-Finland (Paldiski-Hanko)
- Mediterranean France-Tunisia (Marseille-Tunis)
BRITTANY FERRIES
Currently, BRITTANY FERRIES ships operate on the following routes:

- Roscoff-Cork Ireland-Roscoff (crossing time 14 hours)
- Cherbourg-Portsmouth England-Cherbourg (3 hours)
- Roscoff-Plymouth-Roscoff (6 hours)
- Portsmouth-Roscoff-Bilbao-Portsmouth (24-36 hours)
- Portsmouth-Le Havre Paris (5,5 hours)
- Plymouth-Santander Spain-Plymouth (20 hours)
- Portsmouth-Santander-Portsmouth (24 hours)
- Cherbourg-Poole England-Cherbourg (4 hours)
- Saint Malo-Portsmouth-Saint Malo (11 overnights, 8 days)
- Caen-Portsmouth-Caen (6 hours)
- Portsmouth-Le Havre (5,5 days / 8 overnights)
- Cork-Roscoff (1 weekly return-crossing)
- Rosslare-Cherbourg-Bilbao
- Bilbao-Poole UK-Bilbao (freight-only)
BC FERRIES
BC FERRIES' largest ships operate on the following routes (daily service):

- Vancouver Island (between Tsawwassen and Swartz Bay / Victoria BC) - crossing time 1,5 hours, distance 45 km (28 mi)
- Vancouver Island (between Tsawwassen and Duke Point / Nanaimo BC) - 2 hours, distance 70 km (44 mi)
- Horseshoe Bay-Tsawwassen / between West Vancouver (Metro) and Vancouver Island) - 1 hour 40 min, distance 56 km (35 mi)
- Prince Rupert-Port Hardy / Kaien Island-Vancouver Island) - "Day Cruise" Inside Passage (overnight), distance 507 km (315 mi) - Port Hardy, Bella Bella (Campbell Island), Klemtu (Swindle Island), Prince Rupert.
- Prince Rupert-Skidegate Graham Island / Haida Gwaii, crossing time 7 hours, distance 172 km (107 mi)
The company connects mainland British Columbia with the Gulf Islands Cortes, Denman, Hornby, Quadra, Sointula, Texada, Bowen, Gabriola, Galiano, Mayne, Pender, Salt Spring, Saturna, Thetis. The list of destinations also includes Cariboo Chilcotin Coast, Sunshine Coast, Coast Mountains, Vancouver Metro, Northern BC, Thompson Okanagan, Victoria Harbour, and Vancouver Island.
PandO FERRIES
Currently, P&O FERRIES ships operate on the following routes:

- UK to France (Dover-Calais)
- mini cruises England UK to Holland (Hull-Rotterdam) - crossing time 10 hours
- England to Ireland (Liverpool-Dublin)
- Scotland UK to Northern Ireland (Cairnryan-Larne)
- freight ferry service UK-Belgium (London Tilbury-Zeebrugge)
TALLINK-SILJA LINE
Currently, TALLINK-SILJA LINE ships operate on the following cruise ferry routes:

- Finland-Sweden (Helsinki-Aland (Mariehamn)-Stockholm (crossing time 16 hours)
- Finland-Sweden (Turku-Aland (Mariehamn or Langnas)-Stockholm (10,5 hours)
- Estonia-Sweden (Tallinn-Mariehamn Aland-Stockholm (15,5 hours)
- Sweden-Latvia (Stockholm-Riga (17 hours)
- Finland-Estonia (Helsinki-Tallinn (2 hours)
FINNLINES
Currently, FINNLINES ships operate on the following passenger ferry routes:

- Finland-Germany (Helsinki-Travemunde) crossing time 27-29 hours
- Finland-Sweden (Naantali-Kapellskar via Langnas Aland) 8-9 hours
- Sweden-Germany (Malmo-Travemunde) 9 hours
Freight-only services are offered on the routes Finland-Poland (Helsinki-Gdynia, with 3-4 weekly departures) and Finland-Denmark (Helsinki-Aarhus, with 2 weekly departures).
COLOR LINE
Currently, COLOR LINE ships operate on the following passenger ferry routes:

- (Norway-Germany / Oslo-Kiel) crossing time 20 hours
- (Norway-Sweden / Sandefjord-Stromstad) 2,5 hours
- (Norway-Denmark / Kristiansand-Hirtshals) 3 hours 15 min
- (Norway-Denmark / Larvik-Hirtshals) 3 hours 45 min
MOBY LINES
Currently, MOBY LINES ships operate on the following ferry routes:

- Santa Teresa di Gallura-Bonifacio Corsica
- Piombino-Cavo Elba Island
- Piombino-Portoferraio Elba (crossing time 1 hour)
- Livorno-Bastia Corsica (4,5 hours)
- Livorno-Olbia Sardinia / Olbia-Genoa (6-6,5 / 10,5 hours)
- Genoa-Olbia Sardinia (10,5 hours)
- Civitavecchia Rome-Olbia Sardinia (5,5-6,5-8 hours / day and night crossings)
- Livorno-Olbia / Piombino-Olbia (5-6 hours)
- Livorno-Olbia Sardinia (6 hours)
- Genoa-Bastia Corsica (5 hours)
- Nice France-Bastia Corsica (5 hours)
- St Petersburg Russia-Helsinki Finland-Stockholm Sweden-Tallinn Estonia (62,5 hours)
GRIMALDI LINES
Currently, GRIMALDI LINE ships operate on the following routes:

- Italy-Spain - Civitavecchia-Porto Torres (Sardinia)-Barcelona / crossing time 20 hours)
- Italy-Spain (Savona-Barcelona / 17 hours)
- Italy-Morocco - Savona-(Barcelona)-Tangier / 32 hours
- Italy-Tunisia via Sicily - Civitavecchia-Palermo-Tunis (18,5 hours), Salerno-Palermo-Tunis (16,5 hours) - including freight-only
- Sardinia-Italy (Porto Torres-Civitavecchia / 7 hours 15 min)
- Sardinia-Spain (Porto Torres-Barcelona / 11 hours 45 min)
- Sardinia-Italy (Olbia-Livorno / 8 hours 15 min)
- Sardinia-Italy (Olbia-Civitavecchia / 6,5 hours)
- Italy-Sicily (Livorno-Palermo / 18 hours)
- Italy-Greece (Brindisi-Corfu Island-Igoumenitsa / 30,5 hours) and Venice-Ancona-Igoumenitsa-Patras (36 hours)
- Greece-Crete (Piraeus-Chania / ~9 hours) during summer
GNV (Grandi Navi Veloci)
Currently, GNV ships operate on the following routes:

- Genoa-Palermo Sicily (crossing time 21 hours)
- Genoa-Tunis (Italy-Tunisia /24 hours)
- Genoa-(Barcelona)-Tangier (Italy-Morocco /49,5 hours)
- Genoa-Porto Torres Sardinia (12 hours)
- Genoa-Olbia Sardinia (12 hours)
- Naples-Palermo Sicily (11-13 hours)
- Civitavecchia-Palermo-Tunis (Italy-Tunisia /25 hours)
- Spain-Balearic Islands routes Valencia-Mallorca-Ibiza (crossing times 5-7 hours to Ibiza, 7-10 hours to Mallorca)
- Barcelona-Tangier (Spain-Morocco /32 hours)
- Sete-(Barcelona)-Tangier (France-Morocco /40 hours)
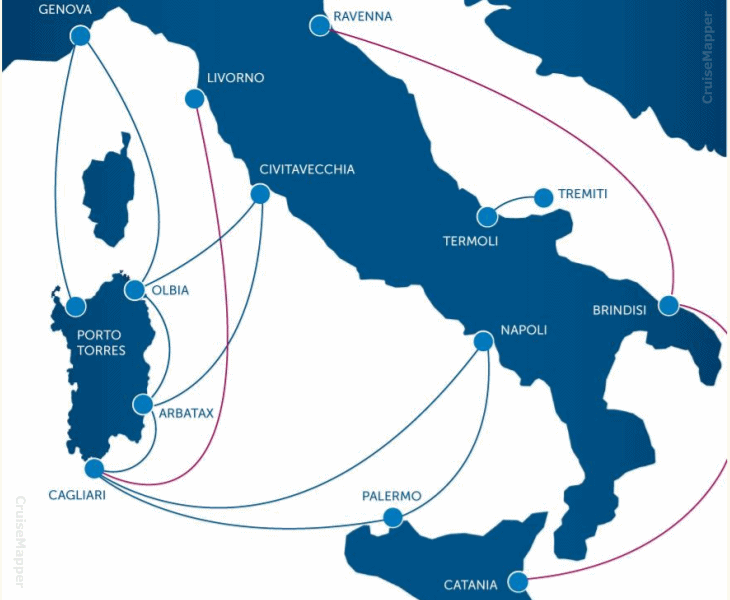
TIRRENIA Navigazione
Currently, TIRRENIA ships operate on the following routes:

- mainland Italy to Sardinia Island - Genoa-Porto Torres (Nuraghes, Sharden), Genoa-Olbia-Arbatax (Athara, Bithia, Janas), Civitavecchia-Olbia-Arbatax (Athara, Bithia, Janas), Civitavecchia-Cagliari (Athara, Bithia, Janas), Naples-Cagliari, Livorno-Cagliari (freight-only)
- mainland Italy to Sicily Island - Naples-Palermo, Ravenna-Brindisi-Catania (freight-only)
- Sardinia to Sicily - Cagliari-Palermo
- mainland Italy (Termoli) to Tremiti Islands
- mainland Italy to Tunisia - Genoa-Tunis
- Sicily to Malta - Catania-Valletta
IRISH FERRIES
Currently, IRISH FERRIES ships operate on the following routes:

- (Ireland-Wales UK) Dublin-Holyhead (crossing time 2 hours)
- (England-France) Dover-Calais (English Channel /2 hours)
- (Ireland-Wales UK) Rosslare-Pembroke (4 hours)
- (Ireland-France) Dublin-Cherbourg, on weekends /19 hours
- (Ireland-Wales UK) Dublin-Holyhead, workweek /2 hours
BALEARIA
Currently, BALEARIA ships operate on the following ferry routes:

- Algeciras to Ceuta and Tangier
- Almeria to Melilla and Nador
- Barcelona to Ibiza, Mallorca, Menorca
- Ceuta to Algeciras
- Denia to Ibiza, Mallorca, Formentera
- Formentera to Ibiza and Denia
- Ibiza to Barcelona, Denia, Mallorca, Formentera, Valencia
- Malaga to Melilla
- Mallorca to Barcelona, Ibiza, Menorca, Denia, and Valencia
- Melilla to Almeria and Malaga
- Menorca to Barcelona and Mallorca
- Valencia to Mallorca, Ibiza, Mostaganem
USA Florida to Bahamas (Fort Lauderdale to Freeport Grand Bahama and to Bimini Island) is Balearia's high-speed Bahamas Ferry Service, with crossing times 2,5-3 hours.
TRASMEDITERRANEA
Currently, TRASMEDITERRANEA ships operate on the following routes:

- (roundtrip from Barcelona to) Ibiza, Mahon (Menorca), Palma de Mallorca, Formentera
- (roundtrip from Palma de Mallorca to) Ibiza, Mahon (Menorca)
- (roundtrip from Valencia to) Ibiza, Mahon (via Palma), Formentera
- roundtrip from Cadiz to Arrecife
- Cadiz-Las Palmas (via Arrecife), Cadiz- Tenerife (via Las Palmas), Cadiz-La Palma (via Arrecife, Las Palmas, Tenerife), Cadiz-Fuerteventura (via Arrecife, Las Palmas, Tenerife, La Palma)
- (from Lanzarote Island) Arrecife-Las Palmas, Arrecife-Tenerife (via Las Palmas), Arrecife-La Palma (via Las Palmas, Tenerife), Arrecife-Fuerteventura (via Las Palmas, Tenerife, La Palma)
- (from Gran Canaria Island) Las Palmas-Tenerife, Las Palmas-La Palma (via Tenerife), Las Palmas-Fuerteventura, Las Palmas-Arrecife (via Tenerife, Fuerteventura), Las Palmas-Cadiz (via Fuerteventura, Arrecife)
- (from Tenerife Island) Santa Cruz de Tenerife-Las Palmas, Tenerife-Fuerteventura (via Las Palmas), Tenerife-Arrecife (via Las Palmas, Fuerteventura), Tenerife-Cadiz (via Gran Canaria , Fuerteventura, Lanzarote)
- (from San Miguel de La Palma Island) Santa Cruz de la Palma-Las Palmas (via Tenerife), La Palma-Puerto Rosario-Fuerteventura (via Tenerife, Las Palmas), La Palma-Arrecife (via Tenerife, Las Palmas, Puerto Rosario, Fuerteventura), La Palma-Cadiz (via Tenerife, Las Palmas, Fuerteventura, Arrecife)
- (from Fuerteventura Island) Puerto del Rosario-Arrecife, Fuerteventura-Cadiz (via Arrecife)
- Algeciras-Ceuta (Spanish Morocco), Algeciras-Tangier (Morocco)
- Almeria-Melilla (Spanish Morocco), Almeria-Ghazaouet (Algeria), Almeria-Nador (Morocco), Almeria-Oran (Algeria)
- Malaga-Melilla
CORSICA-SARDINIA FERRIES
Currently, CORSICA-SARDINIA FERRIES ships operate on the following routes:

Between mainland France-Italy and Corsica Island (In brackets are crossing times)
- between Nice and Ajaccio (6 hours), Bastia (5 hours), Calvi (4 hours), Ile Rousse (4 hours), Porto Vecchio (9 hours)
- between Toulon and Ajaccio (6,5 hours), Bastia (8,5 hours), Ile Rousse (6 hours 15 min), Porto Vecchio (12 hours)
- between Savona and Bastia (4,5 hours), Calvi (6 hours)
- Livorno-Bastia (3,5 hours)
- Piombino-Bastia (2 hours 15 min)
Between mainland Italy-France and Sardinia Island
- Livorno-Golfo Aranci (6,5 hours)
- Toulon-Porto Torres (13 hours)
- Nice-Golfo Aranci (16 hours)
Elba Island (Portoferraio) to/from Piombino (30 min) and Bastia (90 min).
CORSICA LINEA
CORSICA LINEA operates on the Mediterranean Sea routes only, connecting mainland France (Marseille) with Corsica Island (France), Sardinia Island (Italy) and North Africa (Arab Maghreb) - Algeria and Tunisia.

Corsica Linea ferry links include:
- Marseille-Corsica (Ajaccio)
- Marseille-Corsica (Bastia)
- Marseille-Algeria (Algiers) / including seasonal-only crossings
- Marseille-Tunis / including seasonal-only crossings
- Marseille-Algeria (Bejaia) / seasonal-only crossings
- Marseille-Ile Rousse - Monte d'Oro
- Corsica-Sardinia (Ajaccio-Porto Torres)
NAVIERA ARMAS
NAVIERA ARMAS operates mainly inter-island shipping services in the Canary Islands, also connecting the Canaries with Iberia (mainland Spain and Portugal) and North Africa (Morocco).

- Las Palmas (Gran Canaria) - Morro Jable (Fuerteventura) / crossing time 5 hours
- Las Palmas - Santa Cruz de Tenerife /2 hours
- Santa Cruz de Tenerife - Morro Jable (Fuerteventura) Las Palmas /2,5 hours
- Los Christianos (Tenerife)-San Sebastian (La Gomera)
- Motril (Granada)-Nador (Morocco) /6 hours
- Motril - Melilla (Spanish Morocco) /6 hours
- Huelva (Spain)-Tenerife -Gran Canaria /36-37 hours
MINOAN LINES
Currently, MINOAN LINES ships operate on the following routes:

- (Greece-Crete) Piraeus-Heraklion / crossing time 6 hours
- (Greece-Italy) Patras-Igoumenitsa-Ancona-Trieste / 29,5 hours (22 hours to Ancona)
BLUE STAR FERRIES
Currently, BLUE STAR FERRIES ships operate on the following routes:

Note: All departures to the Greek Islands are roundtrips from Port Piraeus (Athens).
- (Greece to Crete) Piraeus-Heraklion
- (Greece to Crete) Piraeus-Chania
- (Greece to Cyclades Islands) Piraeus-Syros-Tinos-Mykonos / crossing time 6 hours
- (Greece to Cyclades Islands) Piraeus-Syros-Paros-Naxos-Ios-Santorini-Anafi) / 8 hours
- (Greece to Cyclades Islands) Piraeus-Syros-Paros-Naxos-Santorini-Irakleia-Schoinoussa-Koufonisia-Donousa-Amorgos-Astypalaia
- (Greece to Dodecanese Islands) Piraeus-Samos-Kos-Rhodes-Karpathos / 20 hours
- (Greece to Dodecanese Islands) Piraeus-Kalymnos-Kos-Rhodes-Astypalaia-Patmos-Lipsi/Leipsoi-Leros-Nisyros-Symi-Tilos-Kastellorizo / 23 hours
- (Greece to North Aegean Islands) Piraeus-Psara-Oinousses-Chios-Lesbos / 12 hours
- roundtrip Piraeus-Kalymnos-Kos-Rhodes-Ikaria-Fournoi Korseon (archipelago)-Astypalaia-Patmos-Lipsi/Leipsoi-Leros-Nisyros-Tilos-Symi-Karpathos-Kasos-Kastellorizo
- roundtrip Piraeus-Syros-Tinos-Mykonos-Ikaria-Samos / 9 hours
ANEK LINES
Currently, ANEK LINE ships operate on the following routes:

- (Greece to Crete) Piraeus-Chania and Piraeus-Heraklion
- (Greek Islands) Piraeus-Milos-Santorini-Kasos-Karpathos-Halki-Rhodes and Piraeus-Milos-Santorini-Anafi-Crete (Heraklion, Sitia)-Kasos-Karpathos-Rhodes
- (Greece-Italy) Patras-Ancona (via Igoumenitsa)
- Greece-Italy) Patras-Venice (via Igoumenitsa)
SUPERFAST FERRIES
Currently, SUPERFAST FERRIES ships operate on the following routes:

Italy-Greece (Bari-Igoumenitsa-Patras) crossing time is 16,5 hours
Italy-Greece (Ancona-Igoumenitsa-Patras) crossing time is 22,5 hours
SEAJETS FERRIES GREECE
SEAJETS FERRIES ships operate exclusively on inter-island routes in Greece's Cyclades Archipelago (including Crete).

Roundtrips from Piraeus-Athens connect to the islands Syros-Mykonos-Naxos-Santorini, also to Sifnos-Serifos-Milos and to Gytheio/Gythio-Kythira-Antikythera-Crete (Kissamos).
Roundtrips from Lavrion connect to the islands Kea-Kythnos-Andros-Tinos-Syros-Paros-Naxos-Donousa-Amorgos-Koufonisia-Schoinoussa (Schinoussa)-Irakleia (Heraklia)-Folegandros-Sikinos-Ios-Thirassia-Santorini-Anafi, and also to Agios Efstratios-Lemnos-Kavala (mainland).
Roundtrips from Heraklion Crete connect to Santorini.
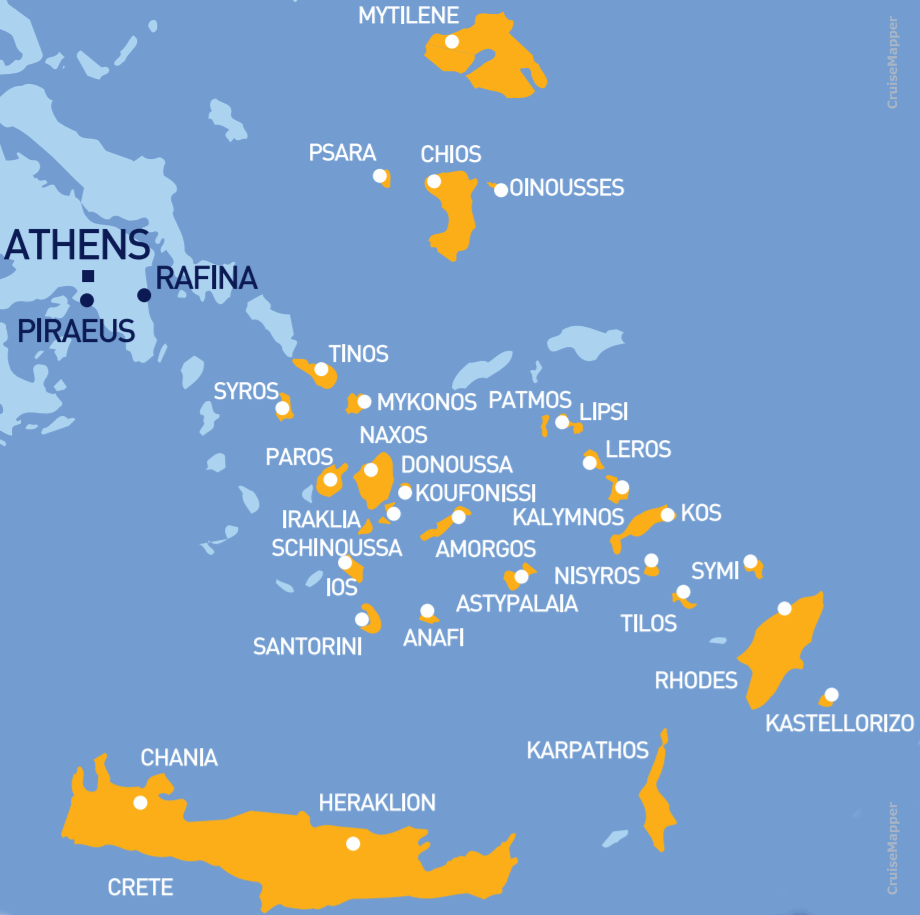
The following map shows all Greek island ferry ports served by ships leaving from mainland Greece (Piraeus and Rafina).
MOL FERRIES Japan
MOL FERRIES is Japan's largest (by fleet and capacity) RoPax shipping company and is owned by MOL Group (MOL-Mitsui OSK Lines).

Currently, MOL FERRIES provides regularly scheduled connections on the following Japanese routes:
Osaka-Beppu (route distance 260 mi / 418 km, crossing time 12 hours), ships Sunflower Kurenai, Sunflower Murasaki
Osaka-Shibushi (route distance 340 mi / 545 km, crossing time 11 hours), ships Sunflower Satsuma, Sunflower Kirishima
Kobe-Oita (route distance 230 mi / 370 km, crossing time 11,5 hours), ships Sunflower Gold, Sunflower Pearl
Oarai-Tomakomai (route distance 470 mi / 755 km, crossing time 18 hours), 12x weekly crossings, ships Sunflower Furano, Sunflower Sapporo
Tokyo-Hokkaido (route distance 890 mi / 1430 km, crossing time 18 hours)
Small-fleet ferry company routes
Follows a list of small-fleet companies ships and routes.
DESTINATION GOTLAND (Sweden) operates the route Visby-Nynashamn (port to Oskarshamn and Vastervik) - crossing time 3 hours.
CONDOR FERRIES operates between UK-France and Channel Islands - Jersey (St Helier Port) and Guernsey (St Peter Port). Fast ferry Condor Liberation serves the route Poole England-Channel Islands. Fast ferry Condor Rapide serves the route St Malo France-Channel Islands. The inter-island service Guernsey-Jersey is 1 hour (on the fast ferries) and 2 hours (on Commodore Clipper). Commodore Clipper and Commodore Goodwill serve the route Portsmouth England-Channel Islands (crossing time 7 hours).
POLFERRIES operate between Poland and Sweden, connecting the ports Swinoujscie-Ystad (crossing time 6 hours) and Gdansk-Nynashamn (crossing time 19 hours).
MARINE ATLANTIC (Canada) operates regular services across Cabot Strait (on the route Nova Scotia-Newfoundland Island) connecting the ports North Sydney-Port aux Basques, and North Sydney-Argentia (Placentia). Crossing times are, respectively, 7 hours (year-round, 7 days a week) and 14-16 hours (summer-only / June through September, 3 days a week).
TT-LINE Tasmania operates exclusively Bass Strait crossings between Devonport (Tasmania) and Melbourne/Geelong (Victoria Australia).
Ferries related cruise news
- Cruise Industry

Stena Line completes refurbishment of Stena Germanica and Stena Scandinavica
Stena Line has completed a significant programme of refurbishment and modernisation on its ferries Stena Germanica and Stena Scandinavica, which...
February 14, 2026 - Accidents

Search suspended after passenger reported overboard from P&O Ferries' European Highlander
A multi‑agency search and rescue operation in the Irish Sea has been stood down after extensive efforts failed to locate an individual reported to...
February 13, 2026 - Accidents

Rescue at sea by MV Isle of Islay during delivery passage to Scotland
During its delivery passage to Scotland, the new CalMac ferry MV Isle of Islay participated in the recovery of a man from the sea off the coast of...
February 9, 2026 - Accidents

Ferry services suspended in the Strait of Gibraltar as Storm Marta impacts maritime links
Maritime traffic across the Strait of Gibraltar was disrupted on February 7th, when strong winds and rough seas due to Storm Marta rendered ferry...
February 8, 2026 - Cruise Industry

18 confirmed dead after ferry Trisha Kerstin 3 sinks off Basilan, Philippines
In the early hours of Monday, January 26th, the Ro-Pax ferry MV Trisha Kerstin 3 (1995-built, IMO 9125516) foundered in waters off the...
January 26, 2026 - Accidents

(Bluebridge Ferries NZ) Connemara mechanical issues lead to overcapacity on Livia service
The ferry company Bluebridge Cook Strait Ferries has acknowledged an overbooking incident on Sunday, January 11th, that resulted in up to 36...
January 12, 2026 - Accidents

Greek ferry services resume cautiously following weather disruption
Ferry operations in Greece began a gradual resumption on Sunday, January 11th, as strong winds that had previously kept vessels alongside moderated...
January 11, 2026 - Cruise Industry

Karachi ferry terminal inaugurated ahead of Pakistan–Iran passenger service
A newly constructed ferry terminal at Karachi Port Trust has been inaugurated by Federal Minister for Maritime Affairs Muhammad Junaid Anwar Chaudhry...
January 9, 2026 - Accidents

Berthing incident brings Holyhead ferry operations to a halt
Holyhead, the UK’s second busiest passenger ferry port (after Dover), was closed to all ferry traffic following a berthing incident involving...
January 7, 2026 - Accidents

Strong Aegean winds trigger sailing ban at Greek ferry ports
Strong southwesterly winds in the central Aegean Sea led Greek maritime authorities to impose a sailing ban from the main passenger ferry ports near...
January 4, 2026 - show more news
